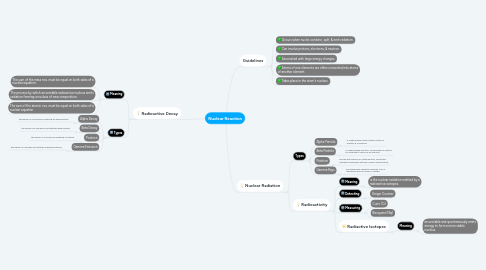
1. Radioactive Decay
1.1. Meaning
1.1.1. The sum of the mass nos. must be equal on both sides of a nuclear equation.
1.1.2. The process by which an unstable radioactive nucleus emits radiation forming a nucleus of new composition.
1.1.3. The sum of the atomic nos. must be equal on both sides of a nuclear equation.
1.2. Types
1.2.1. Alpha Decay
1.2.1.1. the decay of a nucleus by emitting an alpha particle.
1.2.2. Beta Decay
1.2.2.1. the decay of a nucleus by emitting an beta particle.
1.2.3. Positron
1.2.3.1. the decay of a nucleus by emitting a positron.
1.2.4. Gamma Emission
1.2.4.1. the decay of a nucleus by emitting an gamma particle.
2. Guidelines
2.1. Occurs when nuclei combine, split, & emit radiation.
2.2. Can involve protons, electrons, & neutron.
2.3. Associated with large energy changes.
2.4. Atoms of one elements are often converted into atoms of another element.
2.5. Takes place in the atom's nucleus.
3. Nuclear Radiation
3.1. Types
3.1.1. Alpha Particle
3.1.1.1. is a high energy particle that contains 2 protons & 2 neutrons.
3.1.2. Beta Particle
3.1.2.1. is a high energy electron; formed when a neutron is converted to proton & an electron.
3.1.3. Positron
3.1.3.1. hold an anti-particle of a beta particle, since their charges are different but their masses are the same.
3.1.4. Gamma Rays
3.1.4.1. are high energy radiation released from a radioactive have no mass or charge.
3.2. Radioactivity
3.2.1. Meaning
3.2.1.1. is the nuclear radiation emitted by a radioactive isotopes.
3.2.2. Detecting
3.2.2.1. Geiger Counter
3.2.3. Measuring
3.2.3.1. Curie (Ci)
3.2.3.2. Becquerel (Bq)
3.2.4. Radiactive Isotopes
3.2.4.1. Meaning
3.2.4.1.1. an unstable and spontaneously emits energy to form a more stable nucleus.

