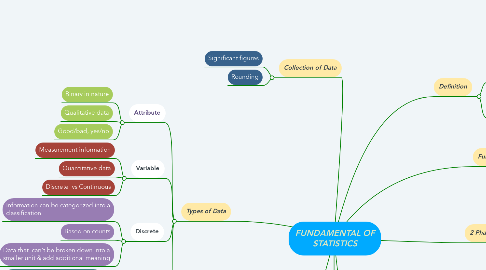
1. Types of Data
1.1. Attribute
1.1.1. Binary in nature
1.1.2. Qualitative data
1.1.3. Good/bad, yes/no
1.2. Variable
1.2.1. Measurement information
1.2.2. Quantitative data
1.2.3. Discrete vs Continuous
1.3. Discrete
1.3.1. Information can be categorized into a classification
1.3.2. Based on counts
1.3.3. Data that can't be broken down into a smaller unit & add additional meaning
1.4. Continuous
1.4.1. Information can be measured on a continuum or scale
1.4.2. Any numeric value
1.4.3. Data that can be measured & broken down into smaller parts & still have meaning
2. Collection of Data
2.1. Significant figures
2.2. Rounding
3. Significant Figures
3.1. Significant Figures = Measured numbers
3.2. To indicate the amount of variation which is allowed in a number
3.3. Closer to the actual value
3.4. Use scientific notation
3.5. If the last digit >=5 then round up, else round down
4. Definition
4.1. Collection of quantitative data pertaining to a subject or group.
4.2. The science that deals with the collection, tabulation, analysis, interpretation, & presentation of quantitative data.
5. Function to :
5.1. organize numerical information in the form of tables, graphs, & charts.
5.2. understand statistical techniques underlying decisions that affect our lives & well-being.
5.3. make informed decisions.
6. 2 Phases
6.1. Descriptive Statistics
6.1.1. Describe characteristics of product or process
6.2. Inferential Statistics (Inductive)
6.2.1. Draw conclusions on unknown process parameters
6.2.2. Uses probability
7. Accuracy & Precision
7.1. Accuracy
7.1.1. Determined by how close a measured value to its "true" vale
7.2. Precision
7.2.1. Determined by how reproducible is the measurement value
8. Describing Data
8.1. Graphical
8.1.1. Frequency distribution
8.1.1.1. Categorical frequency distributions
8.1.1.1.1. Primarily for nominal, ordinal level data
8.1.1.2. Ungrouped frequency distributions
8.1.1.2.1. Range of data is small, single data values for each class
8.1.1.3. Group frequency distributions
8.1.1.3.1. Range of data is large
8.2. Analytical
8.2.1. Measures of central tendency
8.2.1.1. Average
8.2.1.2. Median
8.2.1.3. Mode
8.2.2. Measures of dispersion
8.2.2.1. Range
8.2.2.2. Standard Deviation
8.2.2.3. Variance

