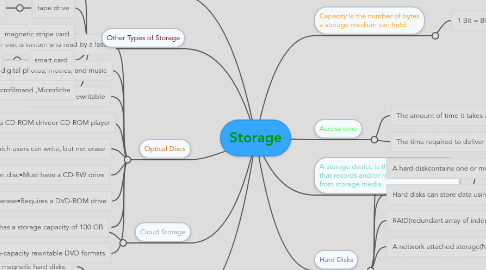
1. Storage holds data, instructions, and information for future use. A storage mediumis the physical material on which a computer keeps data, instructions, and information.
2. Flash Memory Storage
2.1. Solid state drives (SSDs) have several advantages over magnetic hard disks.
2.1.1. Faster access time
2.1.2. Faster transfer rates
2.1.3. Generate less heat and consume less power
2.1.4. Last longer
2.2. USB flash drives
2.2.1. Drivesplug into a USB port on a computer or mobile device
2.3. ExpressCardmodule
2.3.1. Is a removable device that fits in an ExpressCardslot
3. Cloud Storage
3.1. Is an Internet service that provides storage to computer users
4. Optical Discs
4.1. An optical disc consists of a flat, round, portable disc made of metal, plastic, and lacquer that is written and read by a laser
4.2. Typically store software, data, digital photos, movies, and music
4.3. Read only vs. rewritable
4.4. A CD‐ROM can be read from but not written to•Read from a CD‐ROM driveor CD‐ROM player
4.5. A CD‐R is a multisession optical disc on which users can write, but not erase
4.6. A CD‐RW is an erasable multisession disc•Must have a CD‐RW drive
4.7. A DVD‐ROM is a high‐capacity optical disc on which users can read but not write or erase•Requires a DVD‐ROM drive
4.8. A Blu‐ray Disc‐ROM (BD‐ROM) has a storage capacity of 100 GB
4.9. DVD‐RW, DVD+RW, and DVD+RAM are high‐capacity rewritable DVD formats
5. Other Types of Storage
5.1. Tape
5.1.1. Is a magnetically coated ribbon of plastic capable of storing large amounts of data and information
5.2. tape drive
5.2.1. reads and writes data and information on a tape
5.3. magnetic stripe card
5.3.1. Contains a magnetic stripe that stores information
5.4. smart card
5.4.1. Stores data on a thin microprocessor embedded in the card
5.5. Microfilmand ,Microfiche
5.5.1. Store microscopic images of documents on a roll or sheet flim
6. Capacity Is the number of bytes a storage medium can hold.
6.1. 1 Bit = Binary Digit 8 Bits = 1 Byte
6.1.1. 1024 Bytes = 1 Kilobyte
6.1.2. 1024 Kilobytes = 1 Megabyte
6.1.3. 1024 Megabytes = 1 Gigabyte
6.1.4. 1024 Gigabytes = 1 Terabyte
6.1.5. 1024 Terabytes = 1 Petabyte
6.1.6. 1024 Petabytes = 1 Exabyte
6.1.7. 1024 Exabytes = 1 Zettabyte
6.1.8. 1024 Zettabytes = 1 Yottabyte
6.1.9. 1024 Yottabytes = 1 Brontobyte
6.1.10. 1024 Brontobytes = 1 Geopbyte
7. A storage device is the computer hardware that records and/or retrieves items to and from storage media.
7.1. Readingis the process of transferring items from a storage medium into memory.
7.2. Writingis the process of transferring items from memory to a storage medium.
8. Access time
8.1. The amount of time it takes a storage device to locate an item on a storage medium.
8.2. The time required to deliver an item from memory to the processor.
9. Hard Disks
9.1. A hard diskcontains one or more inflexible, circular platters that use magnetic particles to store data, instructions, and information.
9.2. Hard disks can store data using longitudinal recording or perpendicular recording.
9.3. RAID(redundant array of independent disks) is a group of two or more integrated hard disks.
9.4. A network attached storage(NAS) device is a server connected to a network with the sole purpose of providing storage.
9.5. A disk controller consists of a special‐purpose chip and electronic circuits that control the transfer of data, instructions, and information from a disk to and from the system bus and other components of the computer.
9.5.1. SATA
9.5.2. EIDE
9.5.3. SCSI
9.5.4. SAS
