Quadratic Functions
by Alexis Mahlam
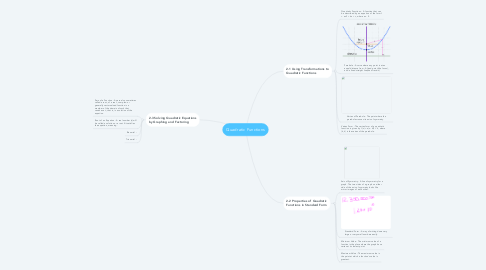
1. 2-1 Using Transformations to Quadratic Functions
1.1. Quadratic Functions - A function that can be described by an equation of the form f = ax2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0.
1.2. Parabola - A curve where any point is at an equal distance from: A fixed point (the focus), and a fixed straight line(the directrix).
1.3. Vertex of Parabola - The point where the parabola crosses its axis of symmetry.
1.4. Vertex Form - The vertex form of a quadratic function is given by f (x) = a(x - h)2 + k, where (h, k) is the vertex of the parabola.
2. 2-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
2.1. Axis of Symmetry - A line of symmetry for a graph. The two sides of a graph on either side of the axis of symmetry looks like mirror images of each other.
2.2. Standard Form - A way of writing down very large or very small numbers easily.
2.3. Minimum Value - The minimum value of a function is the place where the graph has a vertex at its lowest point.
2.4. Maximum Value - The maximum value is the point at which a function's value is greatest.
3. 2-3 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing and Factoring
3.1. Zero of a Function - A zero also sometimes called a root, of a real-, complex- or generally vector-valued function is a member of the domain of such that vanishes at ; that is, is a solution of the equation.
3.2. Root of an Equation - A real number (x) will be called a solution or a root if it satisfies the equation, meaning.
3.3. Binomial -
3.4. Trinomial -


