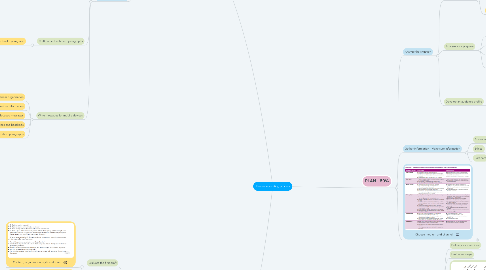
1. WRITE - 25%
1.1. Adapt to your audience
1.1.1. Being sensitive to audience needs
1.1.1.1. Use "you" viewpoint
1.1.1.2. Emphasize the positive
1.1.2. Build strong relationships
1.1.2.1. Establish your credibility
1.1.2.1.1. honesty
1.1.2.1.2. objectivity
1.1.2.1.3. awareness of audience needs
1.1.2.1.4. credentials, knowledge, expertise
1.1.2.1.5. endorsements
1.1.2.1.6. performance
1.1.2.1.7. sincerity
1.1.3. Control your style and tone
1.1.3.1. Create a conversational tone
1.1.3.2. Use a plain language
1.1.3.3. Select active or passive voice
1.2. Compose the message
1.2.1. Choose powerful words
1.2.1.1. Correctness
1.2.1.2. Effectiveness
1.2.1.3. Use jargons carefully
1.2.1.4. Balance abstract vs. concrete words
1.2.1.5. Find words that communicate well
1.2.1.5.1. Avoid cliche and be careful with buzzwords
1.2.1.5.2. Familiar words
1.2.1.5.3. Strong, precise words
1.2.2. Create effective sentences
1.2.2.1. Choose 4 types of sentences
1.2.2.1.1. Simple sentence
1.2.2.1.2. Complex sentence
1.2.2.1.3. Compound sentence
1.2.2.1.4. Compound - complex sentence
1.2.2.2. Use sentence style to emphasize key thoughts
1.2.2.2.1. Devote more words
1.2.2.2.2. Put at the beginning or at the end of the sentence
1.2.2.2.3. Subject of sentence
1.2.3. Craft unified, coherent paragraphs
1.2.3.1. Elements of a paragraph
1.2.3.1.1. Topic sentence
1.2.3.1.2. Support sentences
1.2.3.1.3. Transitions
1.2.4. Write messages for mobile devices
1.2.4.1. Use a linear organization
1.2.4.2. Prioritize information
1.2.4.3. Write short, focused messages
1.2.4.4. Use short subject lines and headlings
1.2.4.5. Use short paragraphs
2. COMPLETE - 25%
2.1. Revise the message
2.1.1. Evaluate the first draft
2.1.1.1. Content, organization, style and tone
2.1.1.2. Evaluate, edit and revise the work of others
2.1.1.2.1. Your job is to help the other succeed, not to impose your writing style
2.1.1.2.2. Make sure you understand the writer's intent before you begin suggesting or making changes
2.1.2. Improve readability
2.1.2.1. Vary sentence length
2.1.2.2. Keep your paragraphs short
2.1.2.3. Use lists to clarify and emphasize
2.1.2.4. Add headings and subheadings
2.1.3. Edit for clarity
2.1.3.1. Edit for conciseness
2.2. Produce the message
2.2.1. Design for readability
2.2.1.1. Consistency
2.2.1.2. Balance
2.2.1.3. Restraint
2.2.1.4. Detail
2.3. Proofread your message
2.4. Distribute the message
2.4.1. Choose a means to distribute messages
2.4.1.1. Cost
2.4.1.2. Convenience
2.4.1.3. Time
2.4.1.4. Security and privacy
3. PLAN - 50%
3.1. Analyze the situation
3.1.1. Define your purpose
3.1.1.1. General purpose
3.1.1.1.1. inform
3.1.1.1.2. persuade
3.1.1.1.3. collaborate
3.1.1.2. Specific purpose
3.1.1.2.1. what you hope to accomplish
3.1.1.2.2. what the audience will do
3.1.1.2.3. what the audience will think
3.1.2. Analyze your purpose
3.1.2.1. will anything change as a result of your message?
3.1.2.2. is your purpose realistic?
3.1.2.3. is the time right?
3.1.2.4. is your purpose acceptable to your organization
3.1.3. Develop an audience profile
3.1.3.1. identify your primary audience
3.1.3.2. determine audience size and geographic distribution
3.1.3.3. determine audience composition
3.1.3.4. estimate audience members' level of understanding
3.1.3.5. understand audience expectations and preferences
3.1.3.6. forecast probable audience reaction
3.2. Gather information - Make sure information
3.2.1. Accurate
3.2.2. Ethical
3.2.3. Pertinent
3.3. Choose medium and channel
3.3.1. Factors to consider
3.3.1.1. Richness
3.3.1.2. Formality
3.3.1.3. Media and channel limitation
3.3.1.4. Urgency
3.3.1.5. Cost
3.3.1.6. Audience preferences
3.3.1.7. Security and privacy
3.4. Organize the information
3.4.1. Define your main idea
3.4.2. Limit your scope
3.4.3. Choose between direct and indirect approaches
3.4.4. Outline your content
3.4.4.1. Start with the main idea
3.4.4.2. State major points
3.4.4.3. Provide examples and evidence
