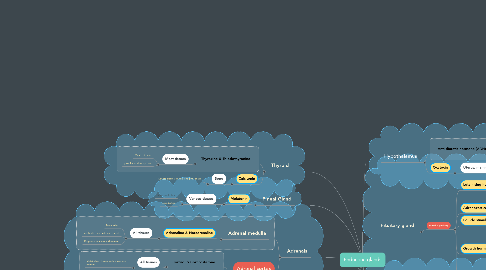
1. Thyroid
1.1. Thyroxine & Triiodothyronine
1.1.1. Most tissues
1.1.1.1. Metabolic rate;
1.1.1.2. growth and development
1.2. Calcitonin
1.2.1. Bone
1.2.1.1. Lowers plasma calcium and phosphate
2. Parathyroid
2.1. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
2.1.1. Bone, kidneys, intestine
2.1.1.1. Elevates plasma calcium and phosphate
3. Thymus
3.1. Thymopoetin
3.1.1. T-lymphocyte cells in blood
3.1.1.1. Immune responses
4. Adrenals
4.1. Adrenal medulla
4.1.1. Adrenaline & Noradrenaline
4.1.1.1. All tissues
4.1.1.1.1. Metabolism
4.1.1.1.2. Involved in heart rate and output
4.1.1.1.3. Response to stress and exercise
4.2. Adrenal cortex
4.2.1. Cortisol & Corticosterone
4.2.1.1. All tissues
4.2.1.1.1. Metabolism; Response to stress and exercise
4.2.2. Aldosterone
4.2.2.1. Primarily kidneys
4.2.2.1.1. Sodium, potassium and pH balance
5. Ovaries (Female)
5.1. Oestrogens
5.1.1. Reproductive organs
5.1.1.1. Reproductive development; also has effects on oestrus behaviour
5.2. Progesterone (from corpus luteum)
5.2.1. Uterus
5.2.1.1. Uterine condition
6. Testes (Male)
6.1. Testosterone
6.1.1. Reproductive organs
6.1.1.1. Reproductive development; also has effects on behaviour
7. Pineal Gland
7.1. Melatonin
7.1.1. Various tissues
7.1.1.1. Circadian rhythm;
7.1.1.2. reproduction
8. DONE BY: Jesrina Sham(1906895F) & Donna Ang (1900774i), Class PE01
9. Posterior pituitary
9.1. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
9.1.1. Kidney tubules
9.1.1.1. Controls Water excretion
9.1.2. Smooth muscle in arterioles
9.1.2.1. Controls Blood pressure
9.2. Oxytocin
9.2.1. Uterine smooth muscle
9.2.1.1. Controls Uterine contractions
9.2.2. Mammary gland
9.2.2.1. Controls Milk ‘let-down’
10. Pituitary gland
10.1. Anterior pituitary
10.1.1. Luteinising hormone (LH)
10.1.1.1. Ovaries
10.1.1.1.1. Causes Ovulation, luteinization of follicle
10.1.1.2. Testes (Leydig cells)
10.1.1.2.1. Causes testosterone secretion
10.1.2. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
10.1.2.1. Adrenal cortex
10.1.2.1.1. Causes Cortisol secretion
10.1.3. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
10.1.3.1. Testes (tubules)
10.1.3.1.1. Causes spermatogenesis
10.1.4. Growth hormone (GH)
10.1.4.1. All tissues
10.1.4.1.1. Ovaries
10.1.4.1.2. Causes growth; carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism
10.1.5. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
10.1.5.1. Thyroid gland
10.1.5.1.1. Causes Thyroxine secretion
11. Hypothalamus
11.1. Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
11.1.1. Kidneys
11.1.1.1. Causes water reabsorption
11.2. Oxytocin
11.2.1. Uterus, mammary glands
11.2.1.1. Stimulates contraction of the uterus in childbirth and is important in breastfeeding.
12. Pancreas
12.1. Insulin (from beta cells)
12.1.1. Most tissues, notably muscle and liver
12.1.1.1. Glucose utilization;
12.1.1.2. Lowers blood glucose level
12.2. Glucagon (from alpha cells)
12.2.1. Primarily liver
12.2.1.1. Elevates blood glucose level

