1. Local Government
1.1. Rural
1.2. Functions in villages
1.2.1. Zila Parishad
1.2.2. Block Samith
1.2.2.1. Gram Panchayat
1.3. Urban
1.3.1. Functions in cities and towns
1.3.1.1. Municipal Corporations (cities)
1.3.1.2. Municipalities (towns)
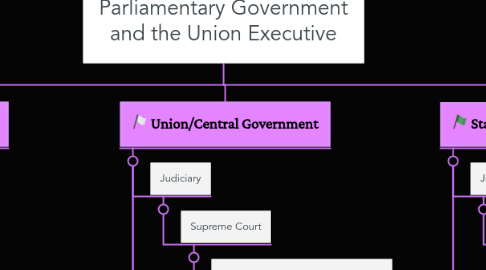
2. Union/Central Government
2.1. Judiciary
2.1.1. Supreme Court
2.1.1.1. Consists of Chief Justice and other supreme court judges
2.2. Executive
2.2.1. Consists of President, Vice-President, Prime Minister and Cabinet Ministers
2.2.1.1. The PM chooses his/her cabinet ministers Lok or Rajya Sabha.
2.2.1.2. The executive is responsible for the day-to-day functions of the country.
2.2.1.3. The vice-president is in charge when the president is ill, gona abroad, or has resigned.
2.3. Legislature
2.3.1. Rajya Sabha
2.3.1.1. Elected by the state legislature
2.3.2. Lok Sabha
2.3.2.1. Elected by the citizens
2.3.3. Together the Lok and Rajya Sabha are called the parliament. They debate laws passed by the executive. This is called a bill. Every member has the opportunity to voice out his/her opinion.
3. State Government
3.1. Judiciary
3.1.1. High Court
3.1.1.1. Consists of chief justice of high court and other high court judges.
3.2. Executive
3.2.1. Consists of the Governor, Chief Minister and Cabinet Ministers.
3.2.1.1. The chief minister elects his/her ministers from the state legislature.
3.2.1.2. The governor is a representative of the union government.
3.3. Legislature
3.3.1. Vidhan Parishad
3.3.1.1. Called MLC's = Members of legislative council
3.3.2. Vidhan Sabha
3.3.2.1. Called MLA's = Members of legislative assembly.
3.3.2.2. Elected by the citizens.

