1. Ethic
1.1. In qualitative research, participants have a vital
1.1.1. Honour the participants’ privacy.
1.1.2. Consider difference in participants’
1.1.3. Protect participants’ identities to avoid embarrassment or harm.
1.1.4. Treat participants with respect and seek their cooperation in the research.
1.1.5. Negotiate with the participants the terms of the agreement to do a study.
1.1.6. Tell the truth when writing up and reporting the findings.
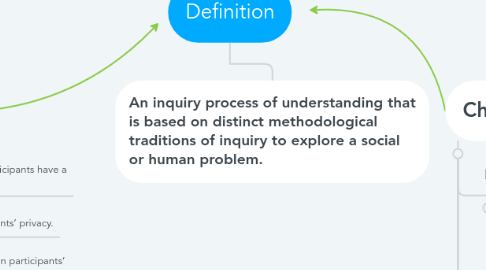
2. An inquiry process of understanding that is based on distinct methodological traditions of inquiry to explore a social or human problem.
3. Characteristics
3.1. Naturalistic
3.1.1. The word naturalistic comes from ecological approaches in biology and is defined as a no experimental approach in which subjects are studied in their natural settings.
3.2. Concern with process
3.2.1. The data could imply interview transcripts, photographs, field notes, videos, personal documents, and other official records.
3.3. Descriptive data
3.3.1. The three main methods of data collection, focus group, in-depth interviews and participant observation, involve more active participation by participants.
3.4. Inductive
3.4.1. This approach uses a bottom-up direction to understand situations, focus on behaviours, construct theories and reach conclusions.
3.5. Meaning
3.5.1. Qualitative researchers know that meaning is of essential concern to the qualitative approach; and that is the reason, why they are really interested in participants’ perspectives
