7.1.3 compare and contrast diverse social and economic structures within the societies of Aboriginal, French and British peoples in pre-Confederation Canada by exploring and reflecting upon the following questions and issues:
by Bill Cosby
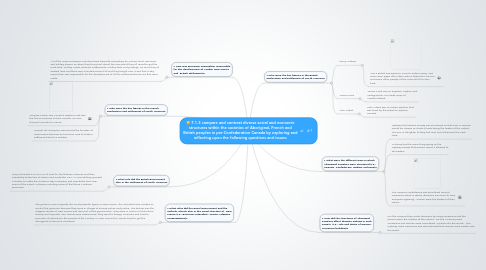

1. • How was European imperialism responsible for the development of Acadia, New France and British settlements?
1.1. All of the major European countries were basically competing for money, land, resources and military power, so when they found out about the new world they all raced to get the most land, so they made colonies, settlements, military forts and postings. So since they all wanted land and there was a limited amount of land they fought over it and that is why imperialism was responsible for the development of all the settlements/colonies that were made.
2. • Who were the key figures in the French exploration and settlement of North America?
2.1. Jacques Cartier was a French explorer and was the first Frenchman to find Canada. He also claimed Canada for France.
2.2. Samuel de Champlain was named the founder of New France because he found an area to make a settlement which is Quebec
3. • What roles did the Royal Government and the Catholic Church play in the social structure of New France (i.e., governor, intendant, Jesuits, religious congregations)?
3.1. The governor was originally the most powerful figure in New France. The Intendant was created so control the governor because they were in charge of money, police and justice. The bishop was the religious leader of New France and also part of the government. They were in control of education, charity and hospitals. The Jesuits were missionaries, they went to foreign countries and tried to promote Christianity to the people of the country. In New France the Jesuits tried to get the aboriginals to become Christians.
4. • What role did the British government play in the settlement of North America?
4.1. They colonized 374704 mi2 of land for the thirteen colonies and then eventually broke free of Britain and made the USA. In Canada they granted a charter to make the Hudson's Bay Company and eventually took over some of the French colonies including some of the future Maritime provinces.
5. • What were the different ways in which Aboriginal societies were structured (i.e., Iroquois Confederacy, Ojibwa, Mi’kmaq)?
5.1. Ojibway first nations society was structured so that men or women would be chosen as chiefs (Chiefs being the leader of the nation). The son or daughter (if they had one) would become the next chief.
5.2. Mi'kmaq has the same thing going as the Ojibway except that women weren't allowed to be leaders.
5.3. The Iroquois confederacy was structured around consensus which is where decisions are come to from everyone agreeing. Women were the leaders of their nation.
6. • How did the structures of Aboriginal societies affect decision making in each society (i.e., role and status of women, consensus building)?
6.1. For the Iroquois they made decisions by using consensus and the women were the leaders of the nations. For the Mi'kmaq used consensus and women were considered "portals into the world". The Ojibway used consensus and also believed that women were portals into the world.
7. • Who were the key figures in the British exploration and settlement of North America?
7.1. Henry Hudson
7.1.1. Was a British sea explorer. Found Hudson's Bay. Was never seen again after other sailors kicked him his son and seven other people of the crew off of his own boat.
7.2. James Cook
7.2.1. James Cook was an explorer, captain and cartographer. He made maps of Newfoundland.
7.3. John Cabot
7.3.1. John Cabot was an Italian explorer that was hired by the British to explore Canada.
