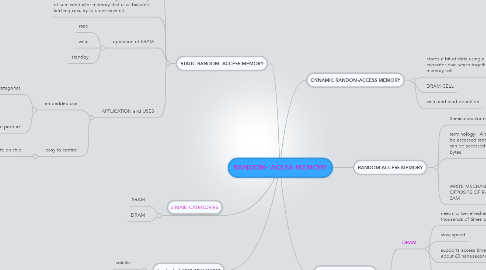
1. 2 MAIN CATEGORIES
1.1. SRAM
1.2. DRAM
2. STATIC RANDOM -ACCESS MEMORY
2.1. a bit of data is stored using the state of a flip-flop.
2.2. Static random-access memory (SRAM) is a type of semiconductor memory that uses bistable latching circuitry to store each bit.
2.3. operation of SRAM
2.3.1. read
2.3.2. write
2.3.3. standby
2.4. APPLICATION and USES
2.4.1. embedded use
2.4.1.1. many categories
2.4.1.1.1. industrial
2.4.1.1.2. scientific subsystems
2.4.1.1.3. automotive electronics
2.4.1.2. general purpose product
2.4.1.2.1. digital camera
2.4.1.2.2. cell phone
2.4.2. easy to control
2.4.2.1. integrate on chip
3. Similarity SRAM AND DRAM
3.1. volatile
3.2. erasure
3.2.1. Electrically, byte-level
4. RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
4.1. Semiconductor memory
4.2. terminology: A type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly; that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes.
4.3. WRITE MECHANISM OPPOSITE OF RAM THAT IS SAM
4.3.1. stores data as a series of memory cells that can only be accessed sequentially
4.3.2. data stored in the order in which it will be used.
4.3.3. works well in memory buffer
5. DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
5.1. stores a bit of data using a transistor and capacitor pair, which together comprise a memory cell.
5.2. DRAM CELL
5.3. write and read operation
6. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SRAM AND DRAM
6.1. DRAM
6.1.1. needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second
6.1.2. slow speed
6.1.3. supports access times of about 60 nanoseconds
6.1.4. less expensive
6.2. SRAM
6.2.1. expensive
6.2.2. can give access times as low as 10 nanoseconds.
6.2.3. does not need to be refreshed
6.2.4. faster
