Malaysia
저자: BiKai Ng
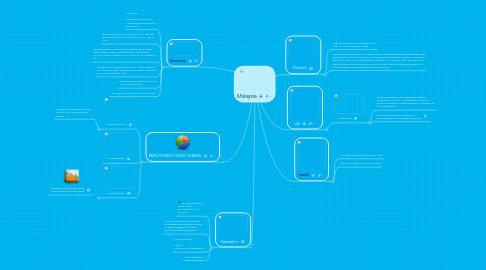

1. EMPLOYMENT STRUCTURE(%)
1.1. 13.2%(agriculture)
1.1.1. Malaysia is responsible for one thirdth of the world's rubber export
1.2. 43.4%(services)
1.3. 43.6%(industry)
1.3.1. malaysia's banking industries have ranked 493 in the world
2. Economy
2.1. GDP rate USD$287,936,971,621 According to the records from 2011.
2.2. Gross per capita income in 2011 at US$9,700 (RM30,623), up from US$6,700 (RM21,152) in 2010.
2.3. Gross domestic product has reached RM881 billion while foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows rose 24.9% to RM36.6 billion in 2011 from RM29.3 billion in 2010
2.4. Malaysia is a country on the move. Often dubbed the "lucky country" because of its wealth of mineral resources and fertile soils
2.5. former mining ground turn in to a recreactional park
2.6. econmy:29 in the world, 3 in theAsean
3. Population
3.1. Has a population of 28.86 million according to 2011 records.
3.2. Almost all malaysians including rural/periphery areas have access To water supply with a rate of 99% of the whole population.
3.3. Life expectancy Age:74 Sources: World DataBank
3.4. literacy rate:88.7
4. health
4.1. Can get medication by post for a fee
4.2. high technology in medical science
5. Problem
5.1. High amounts of CO2 emmission rate With 7.1 metric tons per capita.
5.2. Deforestation problems in Malaysia. forest & jungles are being cut down to make way for palm plantation. which are being exported to other countries to improve the country economy. Deforestation problems in Malaysia. forest & jungles are being cut down to make way for palm plantation. which are being exported to other countries to improve the country economy.
6. Life
6.1. education
6.1.1. Study expenses are low especially in state universities. When it is compared to the same qualified countries, study expenses in Malaysia are more economical.
6.1.2. ensure every child is proficient in bahasa malaysia and english language
