Electromagnetic Waves
by Sean Hö
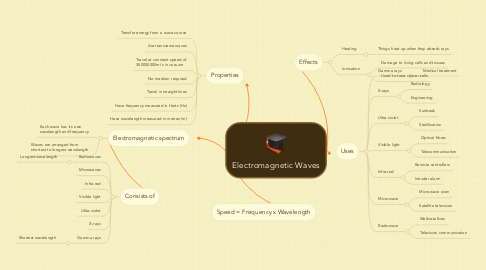

1. Consists of
1.1. Radiowaves
1.1.1. Longest wavelength
1.2. Microwaves
1.3. Infra-red
1.4. Visible light
1.5. Ultra-violet
1.6. X-rays
1.7. Gamma rays
1.7.1. Shortest wavelength
2. Electromagnetic spectrum
2.1. Each wave has its own wavelength and frequency
2.2. Waves are arranged from shortest to longest wavelength
3. Properties
3.1. Transfer energy from a wave source
3.2. Are transverse waves
3.3. Travel at constant speed of 300000000m/s in vacuum
3.4. No medium required
3.5. Travel in straight lines
3.6. Have frequency measured in Hertz (Hz)
3.7. Have wavelength measured in metres (m)
4. Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
5. Effects
5.1. Heating
5.1.1. Things heat up when they absorb rays
5.2. Ionisation
5.2.1. Damage to living cells and tissues
5.2.2. Used to treat cancer cells
6. Uses
6.1. Gamma rays
6.1.1. Medical treatment
6.2. X-rays
6.2.1. Radiology
6.2.2. Engineering
6.3. Ultra-violet
6.3.1. Sunbeds
6.3.2. Sterillisation
6.4. Visible light
6.4.1. Optical fibres
6.4.2. Telecommunication
6.5. Infra-red
6.5.1. Remote controllers
6.5.2. Intruder alarm
6.6. Microwave
6.6.1. Microwave oven
6.6.2. Satellite television
6.7. Radiowave
6.7.1. Walkie-talkies
6.7.2. Television communication
