1. JACOBSON’S anastomosis – connection between n. tympanicus and ganglion oticum
2. ALL BRANCHES DISTALLY TO THE ORIGIN OF THE RECCURENT NERVE, CONVEY PARASYMPATHETIC (=VISCEROMOTOR, GVE) & VISCERAL AFFERENT FIBERS (=VISCEROSENSORY, GVA)
3. Glossopharyngeus
3.1. Course
3.1.1. Sulcus retroolivaris
3.1.1.1. Foramen Jugulare
3.1.1.1.1. 2 ganglia
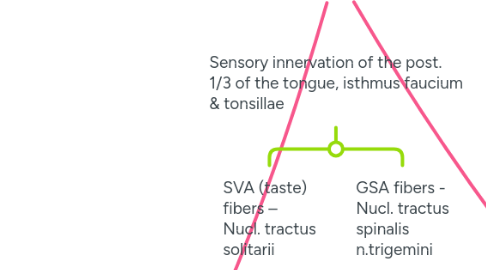
3.2. Innervation
3.2.1. FILL IN ASAP!
3.3. Nuclei
3.3.1. Ambigus
3.3.1.1. SVE
3.3.2. Salivatorius inferior
3.3.2.1. GVE (PS)
3.3.3. Tractus solitarii
3.3.3.1. GVA / SVA (taste)
3.3.4. Spinalis Nervi Trigemini
3.3.4.1. GSA
3.4. Branches
3.4.1. N.Tympanicus
3.4.1.1. branches off, just inf. foramen jugulare
3.4.1.1.1. ascends (within canaliculus tympanicus) into cavitas tympanica
3.4.2. **N. Petrosus Minor**
3.4.2.1. ascends to reach the middle cranial fossa (in sulcus with the same name)
3.4.2.1.1. Foramen lacerum
3.4.3. r. Sinus carotici
3.4.3.1. GVA fibers, originate - SINUS CAROTICUS (pressoreceptors) & GLOMUS CAROTICUM (chemoreceptors)
3.4.3.1.1. perykarya are in ganglion inferius
3.4.4. r. Pharyngei
3.4.4.1. + with rami of N. vagus = **PLEXUS PHARYNGEUS** for motor (SVE) & sensory (GSA) innervation of the pharynx
3.4.4.1.1. also contain GVE (PS) fibers for the pharyngeal glands
3.4.5. r. Tonsilares and Linguales
3.4.6. r. m.stylopharyngei
3.4.6.1. SVE - N. ambigus
4. Vagus
4.1. Course
4.1.1. Longest, neurocranium to abdomen, strongest PS nerve
4.1.1.1. sulcus retroolivarius
4.1.1.1.1. Foramen Jugulare
4.2. Nuclei
4.2.1. Dorsalis Nervi Vagi
4.2.1.1. GVE / PS
4.2.2. Ambigus
4.2.2.1. SVE
4.2.3. Tractus solitarii
4.2.3.1. GVA / SVA (taste)
4.2.4. Spinalis Nervi Trigemini
4.2.4.1. GSA
4.3. Innervation
4.4. Branches
4.4.1. Pars Cranialis
4.4.1.1. R.meningeus
4.4.1.1.1. GSA
4.4.1.2. R. Auricularis
4.4.1.2.1. GSA
4.4.2. Pars cervicalis
4.4.2.1. R. Pharygneus
4.4.2.1.1. SVE/GVA
4.4.2.2. N. Larygneus Superior
4.4.2.2.1. SVE / GVA
4.4.2.3. N. LARYNGEUS RECURRENS dexter
4.4.2.3.1. SVE, GVA, GVE
4.4.2.4. N. LARYNGEUS RECURRENS sinister
4.4.2.4.1. SVE, GVA, GVE
4.4.3. Pars Cervicales / Thoracica
4.4.3.1. Rr. Cardiaci cervicales sup + inf
4.4.3.1.1. Cardiac plexus
4.4.3.2. Rr. Cardiaci thoracici
4.4.3.2.1. GVE / GVA for the heart
4.4.4. Pars Thoracica
4.4.4.1. rr. Bronchiales
4.4.4.1.1. plexus pulmonalis
4.4.4.2. Plexus oesophagus
4.4.5. LASTLY
4.4.5.1. trunus vagalis anterior (left n.X) truncus vagalis posterior ( right n.X) pass through the hiatus oesophageus of diaphragma into the abdominal cavity
4.4.5.1.1. Parasympathetic innervation of abd organs
5. N. Accessorius
5.1. Course
5.1.1. Motor nerve with 2 parts
5.1.1.1. Cranial - Radix cranialis
5.1.1.1.1. axons of nucl. Ambigus (sulcus retroolivaris)
5.1.1.2. 2 merge to from N.11
5.1.1.2.1. cranial / r. internus - pharingeal & laryngeal muscles
5.1.1.2.2. short distance, the spinal root separates + descends as r. externus along the a. carotis interna
5.1.1.3. Spinal - radix spinalis
5.1.1.3.1. • unique - originates extracranally • arises from motor neuron of (C1-C5) • spinal fibers run superiorly and enter the cranial cavity via the foramen magnum
5.2. Paralysis - dropping of shoulders
6. Hypoglossus
6.1. Intro
6.1.1. entirely motor nerve (GSE)
6.1.1.1. innervate all muscles of tongue except palatoglossus
6.1.2. nucleus n. hypoglossi
6.1.2.1. Medulla oblongata
6.2. Course
6.2.1. 10-15 rootles from sulcus anterolateralis between o+p
6.2.1.1. canalis n. hypoglossi
6.2.1.1.1. dorsolaterally in a arc- shape course into Spatium lateropharyngeum
6.3. Ansa cervicalis
6.3.1. fibers of **C1 & C2** (radix superior) also run with n. XII + fibers of **C2 & C3 ** (radix inferior) = **ansa cervicalis**
6.3.1.1. mm. infrahyoidei
6.3.1.2. C1&C2 join to theXII and run to the m. geniohyoideus & m. thyrohyoideus and innervate them
6.4. Paralysis of N.12
6.4.1. m. Genioglossus
