1. REQUIREMENT ENGINEERING: OVERVIEW
1.1. 1📍 Functional Requirements
1.1.1. Description of the software's explicit behaviors, what it should and shouldn't do
1.1.2. Often specific & measurable
1.1.3. These are represented or stated in the form of input to be given to the system, the operation performed and the output expected.
1.1.4. They are the requirements stated by the user which one can see directly in the final product, unlike the non-functional requirements.
1.2. 2📍 Non-functional Requirements
1.2.1. Constraints on the services or functions offered by the software
1.2.1.1. Performance, security, availability
1.2.1.2. Speed, size, ease of use…
1.2.1.3. Applies to the whole software system
1.2.2. Categories
1.2.2.1. **9 categories** of non-functional requirements
1.3. 3📍Examples
1.3.1. Ex1: Online Banking System
1.3.1.1. Functional Requirements
1.3.1.1.1. Users should be able to log in with their username and password.
1.3.1.1.2. Users should be able to check their account balance.
1.3.1.1.3. Users should receive notifications after making a transaction.
1.3.1.2. Non-Functional Requirements
1.3.1.2.1. The system should respond to user actions in less than 2 seconds.
1.3.1.2.2. The system should be able to handle 100 million users with minimal downtime.
1.3.2. Ex2: Food Delivery App
1.3.2.1. Functional Requrements
1.3.2.1.1. Users can browse the menu and place an order.
1.3.2.2. Non- functional Requirements
1.3.2.2.1. The app should load the restaurant menu in under 1 second.
1.3.2.2.2. The system should support up to 50,000 concurrent orders during peak hours.
1.3.2.2.3. The app should be easy to use for first-time users, with an intuitive interface.
2. BUSINESS ANALYSIS: OVERVIEW
2.1. Business case development
2.2. 1📍 Why Outsourcing Business Model and the rise of the BA?
2.2.1. :one: To reduce costs
2.2.1.1. Find developing countries for outsoucing (India, Vietnam)
2.2.2. :two: Lack of senior IT personnels
2.2.2.1. Problems of communication between business and outsource team
2.2.3. :three: Handling of requirements
2.2.3.1. Needs professional staff for better and clearer requirements
2.3. 2📍 Business Life Cycle
2.3.1. :one: Alignment: initial stage
2.3.1.1. :busts_in_silhouette: link an organisation’s strategy to its external environment
2.3.1.2. :warning: A Business Analyst needs to be aware of the external environment and make recommendations for change
2.3.1.3. :pencil2: Eg: A strategy from an Unhappy Bank is to differentiate itself from competitors by offering innovative products and services that cater to the evolving needs of its customers. How to align their digital transformation project into this strategy?
2.3.1.3.1. Review customer feedback to identify areas where a process can be improved
2.3.1.3.2. Conduct market research to identify industry best practices and benchmark against competitors, especially fintechs
2.3.1.3.3. Engage with employees to communicate the proposed change and address any concerns or feedback
2.3.2. :two: **Definition**
2.3.2.1. The elements that will support the change are defined
2.3.2.2. A high level document was prepared that included Unhappy Bank’s vision
2.3.2.3. 💻 Roles of BA
2.3.2.3.1. Define the requirements
2.3.2.3.2. Run a feasibility study and search for options
2.3.2.3.3. Manage stakeholders
2.3.2.3.4. Perform a gap analysis
2.3.3. :three: **Design**
2.3.3.1. Requirements lead to design
2.3.3.1.1. Requirements may be used to define design
2.3.3.1.2. Requirements are focused on needs and design is focused on the solution.
2.3.3.2. 💻 Roles of BA
2.3.3.2.1. Review designs to ensure they align with the requirements.
2.3.4. :four: Implementation
2.3.4.1. The project team with the developers should have a clear tasks to be implemented at this stage
2.3.4.2. 💻 Roles of BA
2.3.4.2.1. Ensure that the development tasks are clear by supporting the project team
2.3.4.2.2. Manage change requests that may arise during the implementation phase, ensuring that any changes align with the overall project objectives.
2.3.5. :five: **Realisation**
2.3.5.1. Once the project is real and the go-live phases have passed, then we needed to ensure that the digital transformation project was successful and had the benefits it was suppose to have.
2.3.5.2. 💻 Roles of BA
2.3.5.2.1. Perform a post implementation review
2.3.6. Business change lifecycle
2.4. 3📍 The range of analysis activities
2.4.1. :one: Strategic Analysis and Definition
2.4.1.1. Consultant’s work, often done by seniors & managers
2.4.2. :two: Business Analysis
2.4.2.1. Resolve business issues
2.4.2.2. Recommend business changes
2.4.2.3. Enhance/replace existing IT system to align with business needs
2.4.2.4. Domain knowledge
2.4.2.5. Stakeholder relationship management
2.4.3. :three: IT system analysis
2.4.3.1. Specification
2.4.3.2. Modelling
2.5. 5📍 BA's Responsibilities
2.5.1. :one: Support the implementation
2.5.1.1. Defining job roles
2.5.1.2. Writing user manuals & guides
2.5.1.3. Developing test scenarios for User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
2.5.1.4. Providing training for new processes & software
2.6. :two: Core responsibilities
2.6.1. Investigate business systems
2.6.2. Evaluate actions to improve business operation
2.6.3. Document the business requirement
2.6.3.1. A document that describes the findings from a business analysis study
2.6.3.2. Recommended course of action for senior management to consider
2.6.4. Elaborate requirements to be up-to-date with user’s business needs and to make a evolutionary system development
2.7. :three: Extended responsibilities (choose 1 to specialize in)
2.7.1. Strategy implementation
2.7.2. Benefit realization
2.7.2.1. Post-implementation reviews
2.7.2.2. Evaluate & report achieved benefits
2.7.3. Specification of IT requirements
2.7.3.1. Modelling
2.7.3.2. UI/UX prototyping
3. BUSINESS OBJECTIVES MODEL
3.1. 1📍 **Purpose**
3.1.1. Allows the stakeholders to identify the value of a project and then to use that value every day to make requirements decisions
3.1.1.1. :package: Box: business problem, objective, or product concept
3.1.1.2. :arrow_right: Arrow: Link between boxes
3.2. **2📍 Business Objectives Model Process**
3.2.1. :one: Starts with a business problem
3.2.2. :two: Followed by at least one business objective
3.2.3. :three: Each business objective can lead to another business problem or to the product concept
3.2.3.1. product concept
3.3. **3📍 Elements of Business Objectives Model**
3.3.1. :one: Business problem
3.3.1.1. Issue preventing the business from achieving its goals
3.3.2. :two: Business objective
3.3.2.1. Measureable target that specifies when the business problem is solved
3.3.2.2. Business Problems
3.3.3. :three: Product concept
3.3.3.1. Vision of the actual solution that the business chooses to implement in order to meet the business objective It is typically described by a list of high-level features
3.3.4. :four: Success metric
3.3.4.1. A business objective that will actually be measured to determine whether the project is successful, or additional measures that are related to the solution
3.4. **4📍 Example: Chemical Tracking System**
3.4.1. **Product Concept**
4. Users can make payments and track their orders in real time.
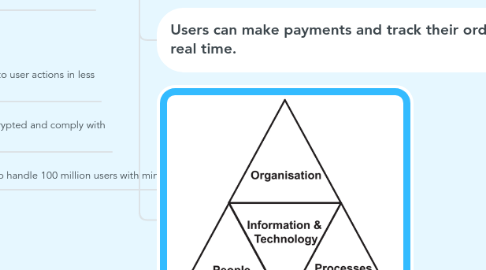
5. 4📍 THE POPIT MODEL APPROACH: 5W5H
5.1. :busts_in_silhouette: Organisation
5.1.1. Structure, resources, roles and responsibilities
5.1.1.1. Are they skillful?
5.1.1.2. Are they motivated?
5.2. ⏳ Processes
5.2.1. Key business processes to deliver products & services to customers
5.2.1.1. How is collaboration?
5.2.1.2. Are they well-defined?
5.2.1.3. Is communication good?
5.2.1.4. Is there IT support?
5.2.1.5. Are responsibility clear?
5.2.1.6. Is management effective?
5.3. :bust_in_silhouette: People
5.3.1. Staff and resources who carry out the work
5.4. :os_win: Information & Technology
5.4.1. Hardware systems and software applications that support the organisation's work
5.4.1.1. 📃 Information
5.4.1.1.1. Require for effectie work
5.4.1.2. **💻 Technology**
5.4.1.2.1. A medium to drive organization's goal
5.5. ❓ **What**
5.5.1. A holistic model that outlines the various dimensions within an organisation
5.6. 🧭 **Where**
5.6.1. Identifies the four domains within the organisation
5.7. ⁉️ Why
5.7.1. Its important to understand all the areas that are impacted due to the implementation of strategy or the change programme
5.8. :bust_in_silhouette: Who
5.8.1. Stakeholders: Senior Management, Executives and Board of directors, Strategic consultants
5.9. :mag: How
5.9.1. Surveying and interviewing
5.10. ⏰ When
5.10.1. In a product development project or change management initiative
