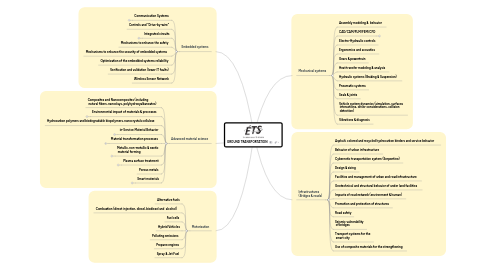
1. Mechanical systems
1.1. Assembly modeling & behavior
1.2. CAD/CAM/PLM/FEM/CFD
1.2.1. Boundary Element Method (BEM)
1.2.2. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
1.2.3. Computer Aided Design (CAD)
1.2.4. Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
1.2.5. Finite Element Modeling (FEM)
1.3. Electro-Hydraulic controls
1.4. Ergonomics and acoustics
1.5. Gears & powertrain
1.6. Heat transfer modeling & analysis
1.7. Hydraulic systems (Braking & Suspension)
1.8. Pneumatic systems
1.9. Seals & joints
1.10. Vehicle system dynamics (simulation, surfaces interactions, driver considerations, collision detection)
1.11. Vibrations & diagnosis
2. Embedded systems
2.1. Communication Systems
2.1.1. Wireless
2.1.2. Satellite, GPS
2.2. Controls and "Drive-by-wire"
2.3. Integrated circuits
2.3.1. Design
2.3.2. Test
2.4. Mechanisms to enhance the safety
2.5. Mechanisms to enhance the security of embedded systems
2.6. Optimization of the embedded systems reliability
2.7. Verification and validation (lower IT faults)
2.8. Wireless Sensor Network
3. Infrastructures (Bridges & roads)
3.1. Asphalt, colored and recycled hydrocarbon binders and service behavior
3.2. Behavior of urban infrastructure
3.3. Cybernetic transportation system (Serpentine)
3.4. Design & sizing
3.5. Facilities and management of urban and road infrastructure
3.6. Geotechnical and structural behavior of under land facilities
3.7. Impacts of road network (environment & human)
3.8. Promotion and protection of structures
3.9. Road safety
3.10. Seismic vulnerability of bridges
3.11. Transport systems for the smart city
3.12. Use of composite materials for the strengthening
4. Advanced material science
4.1. Composites and Nanocomposites (including natural fibers, nanoclays, polyhydroxyalkanoates)
4.2. Environmental impact of materials & processes
4.2.1. Analysis of the sources of air pollution for workers
4.2.2. Clean machining
4.2.3. Management of industrial waste
4.2.4. Nanotoxicology
4.2.5. Treatment of industrial effluents
4.3. Hydrocarbon polymers and biodegradable biopolymers, nanocrystals cellulose
4.4. in-Service Material Behavior
4.4.1. Corrosion
4.4.2. Creep
4.4.3. Fatigue modeling and analysis
4.4.4. Residual stress modeling, analysis and prevention
4.4.5. Rheology
4.4.6. Welding & joints
4.5. Material transformation processes
4.5.1. Additive Manufacturing
4.5.2. Brazing
4.5.3. Contour hardening
4.5.4. Generation of machining lines / manufacturing
4.5.5. High-performance removal of materials
4.5.6. Surface treatment
4.5.7. Welding
4.6. Metallic, non-metallic & exotic material forming
4.6.1. Hot spinning
4.6.2. Hydroforming
4.6.3. Process simulation (FEM, cellular automata, self-consistent models)
4.7. Plasma surface treatment
4.7.1. Hydrophobization cellulosic surfaces (inert and organic materials)
4.7.2. Hydrophobization of surfaces
4.8. Porous metals
4.9. Smart materials
4.9.1. Hydrorheological fluid
4.9.2. Magnetorheological fluids
4.9.3. Nanomaterials
4.9.4. Shape memory alloys

