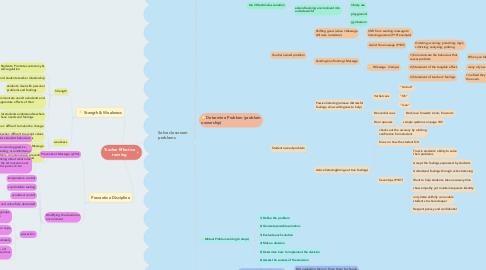
1. Stength & Weakness
1.1. Strength
1.1.1. Students: Promotes autonomy & self-regulation
1.1.2. promotes good students-teacher relationship
1.1.3. students: deal with personal problems and feelings
1.1.4. teacher to communicate need to students and let students appreciate effects of their behaviour
1.1.5. let students understand teachers have needs and feelings
1.2. weakness
1.2.1. teacher: difficult to make the change
1.2.2. Teacher: difficult to accept values different from themselves
1.2.3. Teacher: difficult to master I-Message
1.2.4. More comprehensive preventive discipline may be needed
2. Preventive Discipline
2.1. Preventive I-Message (p194)
2.1.1. modify future student behaviour
2.1.2. Not to sound aggressive, demanding, or authoritarian
2.1.3. eg: I’d appreciate having you begin thinking about what rules may be needed during our field trip to the art museum next week so that any problems that you antici- pate can be prevented.
2.2. Modifying the classroom environment
2.2.1. temperature control
2.2.2. comfortable seating
2.2.3. acoustical control
2.2.4. beautifully and colourfully decorated
2.2.5. places for:
2.2.5.1. students to concentrate, work in groups, build things, experiment, listen to teacher
2.2.5.2. students to let off steam or cope with personal problems
2.2.5.3. teacher to confer with students privately
2.2.5.4. eg. learning centres, libraries, art centres, audiovisual centres, seminar rooms
3. Solve classroom problems
3.1. Roadblocks (block effective communication)
3.1.1. teacher hand out solutions to problems and expect students to accept
3.1.1.1. discounted by students
3.1.1.2. students fell their inadequacy
3.1.2. send indirect message to solve problem
3.1.2.1. kidding;teasing; sarcasm
3.2. Identify student needs (accept students' behaviour as attempt to satisfy needs)
3.2.1. Listen to students carefully and accurately
3.2.2. keep in mind that there's always a reason behind children's behaviour
3.2.3. make clarifying/direct inquiries
3.3. Making a trade
3.3.1. Offer student a new productive task and forget the disruptive one
3.3.1.1. set video instead of disturbing peers
3.4. Modifying the environment
3.4.1. When students are overstimulated
3.4.1.1. allow them to e more active
3.4.1.1.1. role play
3.4.1.1.2. debates
3.4.1.1.3. interviews
3.4.1.1.4. discussions
3.4.2. impoverished school environment (many regulations, rules, procedures)
3.4.2.1. provide students opportunities to learn that they wish
3.4.2.2. allow them have a say in classroom rules and regulations
3.4.3. too little stimulus variation
3.4.3.1. provide different learning activities
3.4.3.2. extend learning environment into outside world
3.4.3.2.1. field trips
3.4.3.2.2. library use
3.4.3.2.3. playground
3.4.3.2.4. gymnasium
3.5. Determine Problem (problem ownership)
3.5.1. Teacher owned problem
3.5.1.1. Shifting gears (when I-Message still raise resistance)
3.5.1.1.1. Shift from sending message to listening posture (P191example)
3.5.1.2. Sending Confronting I-Message
3.5.1.2.1. Avoid You-message (P189)
3.5.1.2.2. I-Message (3 steps)
3.5.2. Student owned problem
3.5.2.1. Passive listening (release distressful feelings; show willingness to help)
3.5.2.1.1. Verbal cues
3.5.2.1.2. Nonverbal cues
3.5.2.1.3. Door openers
3.5.2.2. Active listening(bring out true feelings)
3.5.2.2.1. checks out the accuracy by eliciting verification from student
3.5.2.2.2. focus on how the student felt
3.5.2.2.3. Seven tips (P187)
3.6. Mutual Problem solving (6 steps)
3.6.1. 1) Define the problem
3.6.2. 2) Generate possible solutions
3.6.3. 3) Evaluate each solution
3.6.4. 4) Make a decision
3.6.5. 5) Determine how to implement the decision
3.6.6. 6) Assess the success of the decision
3.7. When values collide
3.7.1. gain acceptance by students as a consultant regarding value matters
3.7.1.1. Not evaluating them or force them to change
3.7.1.2. Prepared and appear knowledgeable
3.7.2. Shift gears and engage active listening when resistance is encountered
3.7.3. Model what your values
3.7.4. Maintain good student-teacher relationships
3.8. Foster self-regulation
3.8.1. Avlid Controlling
3.8.1.1. Punishment
3.8.1.1.1. Obey authority
3.8.1.1.2. Increase misbehaviour
3.8.1.1.3. Crime and injury
3.8.1.1.4. Little self-control
3.8.1.1.5. Aggresion
3.8.1.1.6. When the authority loses power, there are various coping mechanism from students (P178)
3.8.1.2. Rewards
3.8.1.2.1. Grades
3.8.1.2.2. Praise
