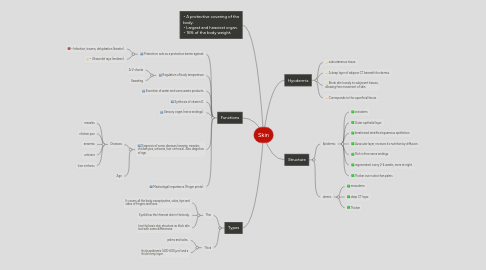
1. Hyodermis
1.1. subcutaneous tissue.
1.2. A deep layer of adipose CT beneath the dermis.
1.3. Binds skin loosely to subjacent tissues, allowing free movement of skin.
1.4. Corresponds to the superficial fascia.
2. • A protective covering of the body. • Largest and heaviest organ. • 16% of the body weight.
3. Structure
3.1. Epidermis
3.1.1. ectoderm.
3.1.2. Outer epithelial layer.
3.1.3. keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
3.1.4. Avascular layer, receives its nutrition by diffusion.
3.1.5. Rich in free nerve endings.
3.1.6. regenerated every 2-4 weeks, more at night.
3.1.7. Thicker over soles than palms
3.2. dermis
3.2.1. mesoderm.
3.2.2. deep CT layer.
3.2.3. Thicker
4. Functions
4.1. Protection: acts as a protective barrier against:
4.1.1. – Infection, trauma, dehydration (keratin).
4.1.2. – Ultraviolet rays (melanin).
4.2. Regulation of body temperature
4.2.1. A-V shunts
4.2.2. Sweating
4.3. Excretion of water and some waste products.
4.4. Synthesis of vitamin D.
4.5. Sensory organ (nerve endings).
4.6. Diagnosis of some diseases (anemia, measles, chicken pox, urticaria, liver cirrhosis). Also diagnosis of age.
4.6.1. Diseases
4.6.1.1. measles
4.6.1.2. chicken pox
4.6.1.3. anaemia
4.6.1.4. urticaria
4.6.1.5. liver cirrhosis
4.6.2. Age
4.7. Medicolegal importance (Finger prints).
5. Types
5.1. Thin
5.1.1. It covers all the body except palms, soles, tips and sides of fingers and toes.
5.1.2. Eyelid has the thinnest skin in the body.
5.1.3. has the basic skin structure as thick skin but with some differences.
5.2. Thick
5.2.1. palms and soles.
5.2.2. thick epidermis (400-600 µm) and a thick horny layer.

