Electromagnetic Radiation
by Meghan Tuttle
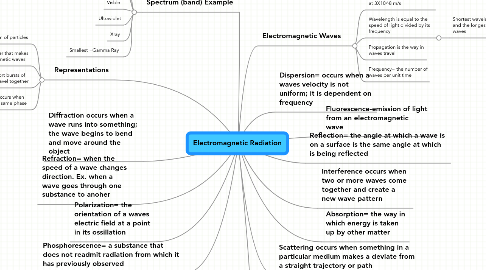

1. Representations
1.1. Ray= narrow beam of particles
1.2. Particle= matter that makes up electromagnetic waves
1.3. Wave Packet= short bursts of waves that also travel together
1.4. Wave Front = occurs when waves have the same phase
2. Refraction= when the speed of a wave changes direction. Ex. when a wave goes through one substance to anoher
3. Diffraction occurs when a wave runs into something; the wave begins to bend and move around the object
4. Spectrum (band) Example
4.1. Largest= Radio
4.2. Microwave
4.3. Infrared
4.4. Visble
4.5. Ultraviolet
4.6. Xray
4.7. Smallest =Gamma Ray
5. Polarization= the orientation of a waves electric field at a point in its ossillation
6. Transparent= ability for light pass through something
6.1. Translucent= allows light to diffuse as it passes through
6.2. Opaque- the amount of light which is blocked
7. Phosphorescence= a substance that does not readmit radiation from which it has previously observed
8. Electromagnetic Waves
8.1. The speed of all waves travel at 3X10^8 m/s
8.2. Wavelength is equal to the speed of light divided by its frequency
8.2.1. Shortest wavelength= gamma rays and the longest wavelength = radio waves
