1. What is social media?
1.1. According to the Society of Human Resources Management defines it as " "web-based tools and technologies used to share information and turn communication into interactive dialogues with internal or external audiences" (SHRM, 2012).
2. Adult Learning Theories
2.1. Behaviorist Theory
2.1.1. Concentrate efforts on observable learner behavior. (Sink, 2008)
2.1.2. Employees will be trained on law enforcement best practices to ensure best results
2.2. Cognitive Learning Theory
2.2.1. Helps us provide conditions that make it more likely learners will acquire the thinking strategies necessary to improve their job performance. (Sink, 2008).
2.2.2. According to Sink, the cognitive approach is well suited to helping learners recall new information, comprehend how things work and use new procedures.
2.3. Constructivist learning Theory
2.3.1. Constructivist learning experiences involve carefully crafted activities, multiple perspectives, and learner-driven knowledge creation. (Sink, 2008)
2.3.2. Employees will experience real-world scenarios and have to transfer their what they have learned to their job functions.
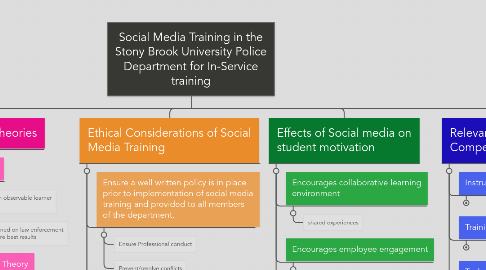
3. Effects of Social media on student motivation
3.1. Encourages collaborative learning environment
3.1.1. shared experiences
3.2. Encourages employee engagement
3.2.1. Increased interaction among members
3.3. Increased student empowerement
4. Ethical Considerations of Social Media Training
4.1. Ensure a well written policy is in place prior to implementation of social media training and provided to all members of the department.
4.1.1. Ensure Professional conduct
4.1.2. Prevent/resolve conflicts
4.2. Provide necessary training to all members of the department
4.2.1. Access to computers and programs
4.3. Confidentiality and Productivity
4.3.1. Employees must be made aware of the guidelines regarding confidentiality
4.3.2. Loss of member productivity must be addressed
5. Relevant Training Program Competencies
5.1. Instructional Design
5.1.1. Employee
5.1.2. Employee
5.2. Training Delivery
5.2.1. Employee
5.2.2. Employee
5.3. Technology skills
5.3.1. Employee
5.3.2. Employee
6. References
6.1. Bingham, T. , & Conner. M. (2010).//The new social learning: A guide to transforming organizations through social media.//Alexandria, VA: ASTD Press.
6.1.1. Bozarth, J. (2010).//Social media for trainers: Techniques for enhancing and extending learning.//San Francisco, CA:Wiley/Pfeiffer
6.1.1.1. Evans Jennings, S., Blount, J., & Weatherly, M. (n.d.). Social media-a virtual pandora's box: prevalence, possible legal liabilities and policies. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 77(1), 96-113. Retrieved March 19, 2016.
6.1.1.1.1. Fiehl, S.. (2012, January 1). Integrating social media, workplace learning, and elearning for development of soft skills. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
