1. Birds and Mammals
1.1. Endotherms and breathe trough lungs
1.1.1. Birds
1.1.1.1. Front limbs are wings
1.1.1.2. Hollow and light bones
1.1.1.3. Toothless mouth whit a beak
1.1.1.4. Scales and feathers
1.1.1.5. Vital functions
1.1.1.5.1. Nutricion
1.1.1.5.2. Reproduction
1.1.1.5.3. Interaction
1.1.1.6. Clasification
1.1.1.6.1. Anseriformes
1.1.1.6.2. Falconiformes
1.1.1.6.3. Galliformes
1.1.1.6.4. Ciconiformes
1.1.1.6.5. Passerines
1.1.2. Mammals
1.1.2.1. Mamary glands = milk feeding
1.1.2.2. Skin covered by hair, fur, or blubber
1.1.2.3. Four legs whit differents shapes and fingers
1.1.2.3.1. Legs
1.1.2.3.2. Arms
1.1.2.3.3. Wings
1.1.2.3.4. Fins
1.1.2.4. Vital functions
1.1.2.4.1. Nutricion
1.1.2.4.2. Reproduction
1.1.2.4.3. Interaction
1.1.2.5. Clasification
1.1.2.5.1. Monotremes
1.1.2.5.2. Marsupials
1.1.2.5.3. Placental mammals
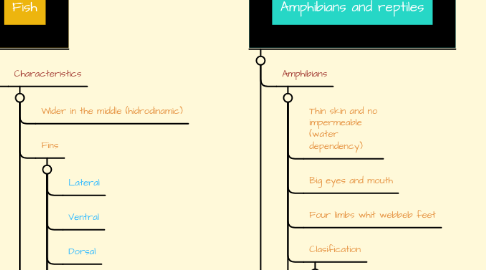
2. Fish
2.1. Characteristics
2.1.1. Wider in the middle (hidrodinamic)
2.1.2. Fins
2.1.2.1. Lateral
2.1.2.2. Ventral
2.1.2.3. Dorsal
2.1.2.4. Caudal
2.1.2.5. Lateral line
2.1.3. Gills
2.1.4. Eggs whit out shells
2.2. Clasification
2.2.1. Bony
2.2.1.1. Bony skeleton
2.2.1.2. Grills covered by operculum
2.2.1.3. Caudal fin divided into two equal sides
2.2.1.4. Trout, hake and salmon
2.2.2. Cartilaginous
2.2.2.1. Cartilaginous skeleton
2.2.2.2. Gills whit out cover
2.2.2.3. Caudal fin divided in unequal sides
2.2.2.4. Shark, ray and manta ray
3. General characteristics
3.1. Multicelulars
3.2. Eukariotes
3.3. Heterothropics
3.4. Animal kingdom
3.4.1. Invertebrates (subphylum)
3.4.2. Vertebrates (subphylum)
3.4.2.1. Fish
3.4.2.2. Amphibians
3.4.2.3. Reptiles
3.4.2.4. Birds
3.4.2.5. Mammals
3.5. Vital functions
3.5.1. Nutricion
3.5.1.1. Heterothropic
3.5.1.2. Nutrients
3.5.1.2.1. Digestive system
3.5.1.3. Gas exchange
3.5.1.3.1. Gills
3.5.1.3.2. Lungs
3.5.2. Interaction
3.5.2.1. Nervous system
3.5.2.1.1. Brain
3.5.2.2. Sense organ
3.5.2.3. Response
3.5.2.4. Spinal cord
3.5.3. Reproduction
3.5.3.1. Sexual
3.5.3.2. Oviparous
3.5.3.3. Viviparous
3.5.3.4. Oviviparous
4. Amphibians and reptiles
4.1. Amphibians
4.1.1. Thin skin and no impermeable (water dependency)
4.1.2. Big eyes and mouth
4.1.3. Four limbs whit webbeb feet
4.1.4. Clasification
4.1.4.1. Anuras (no tail)
4.1.4.1.1. Frogs and toads
4.1.4.1.2. Hind legs are longer
4.1.4.2. Urodela (tail)
4.1.4.2.1. Newts and salamanders
4.1.5. Vital functions
4.1.5.1. Reproduction
4.1.5.1.1. sexual and oviparous
4.1.5.1.2. Metamorphosis
4.1.5.2. Nutricion
4.1.5.2.1. Hervibores (young)
4.1.5.2.2. Carnivores (adults)
4.1.5.3. Interaction
4.1.5.3.1. Vocal cords
4.2. Reptiles
4.2.1. Skin covered by scales
4.2.2. Water independence
4.2.3. Eggs whit hard shell
4.2.4. No methamorphosis
4.2.5. Tail, four limbs and five fingers
4.2.6. Classication:
4.2.6.1. Chelonians (turtles whit caparace)
4.2.6.1.1. Tortoise, turtle and terrapines
4.2.6.2. Snakes (no legs)
4.2.6.2.1. Vipers, cobra and rattle snakes
4.2.6.3. Cocodriles (Big and powerfull jaws)
4.2.6.3.1. Crocodrile, caiman and aligator
4.2.6.4. Lizards (sentive tongue)
4.2.6.4.1. Guecko, iguana and chameleon
