1. Application
1.1. logistics
1.2. payment
1.3. product trackking
1.4. access control
1.5. identification
1.6. asset management
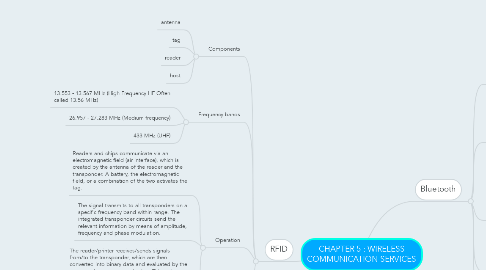
2. RFID
2.1. Components
2.1.1. antenna
2.1.2. tag
2.1.3. reader
2.1.4. host
2.2. Frequency bands
2.2.1. 13.553 - 13.567 MHz (High Frequency HF Often called 13.56 MHz)
2.2.2. 26.957 - 27.283 MHz (Medium frequency)
2.2.3. 433 MHz (UHF)
2.3. Operation
2.3.1. Readers and chips communicate via an electromagnetic field (air interface), which is created by the antenna of the reader and the transponder. A battery, the electromagnetic field, or a combination of the two activates the tag.
2.3.2. The signal transmits to all transponders on a specific frequency band within range. The integrated transponder circuits send the relevant information by means of amplitude, frequency and phase modulation.
2.3.3. The reader/printer receives/sends signals from/to the transponder, which are then converted into binary data and evaluated by the connected computer application. This makes transponders particularly reliable, even in extreme environmental conditions. Other advantages include the fact that no sight contact is required with the reader, the device offers high memory capacity and the potential to capture information from several data carriers at the same time in a single reading process (bulk capturing).
2.4. EPC
2.4.1. Electronic Product Code (EPC) stored in the tag chip's memory is written to the tag by an RFID printer and takes the form of a 96-bit string of data
2.4.2. a)first eight bits are a header which identifies the version of the protocol
2.4.3. b)next 28 bits identify the organization that manages the data for this tag; the organization number is assigned by the EPCglobal consortium
2.4.4. c)next 24 bits are an object class, identifying the kind of product
2.4.5. d)last 36 bits are a unique serial number for a particular tag
3. Bluetooth
3.1. Definition
3.1.1. a standard for the short-range wireless interconnection of cellular phones, computers, and other electronic devices.
3.2. Specifications
3.2.1. 2.4 to 2.485GHz
3.2.2. IEEE 802.15.1
3.2.3. Gaussian frequency-shift keying (GFSK) modulation
3.2.4. packet-based protocol with a master-slave structure
3.3. Application
3.3.1. wireless PC peripheral
3.3.2. military
3.3.3. games
3.3.4. mobile
3.4. Piconet
3.4.1. adhoc network which links a wireless user group of devices using Bluetooth technology protocols
3.5. Scatternet
3.5.1. ad hoc computer network consisting of two or more piconets. The terms 'scatternet' and 'piconet' are typically applied to Bluetooth wireless technology.

