Corrosion
by Alex Udy
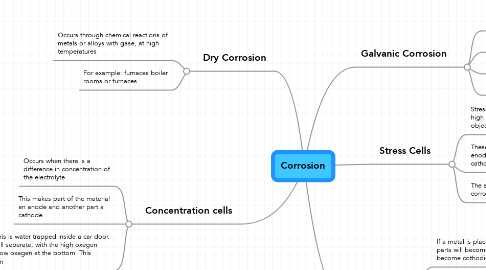
1. Galvanic Corrosion
1.1. Ananode and cathode
1.2. electrolyte
1.3. anode passes elctrons to cathode
1.4. anode corrodes
2. Dry Corrosion
2.1. Occurs through chemical reactions of metals or alloys with gase, at high temperatures
2.2. For example: furnaces boiler rooms or furnaces
3. Uniform Attack
3.1. If a metal is placed in an electrolyte, some parts will become anotic while other become cothodic
3.2. The locations of the cathode and anode will continually change, resulting in uniform corrosion.
3.3. Steel will form a uniform layer of rust under certain circumstances
4. Concentration cells
4.1. Occurs when there is a difference in concentration of the electrolyte
4.2. This makes part of the material an anode and another part a cathode
4.3. A good example of this is water trapped inside a car door. over time the water will seperate; with the high oxegen water at the top and low oxegen at the bottom. This casues the low oxegen
5. Stress Cells
5.1. Stress cells are the result in high stress in parts of a metal object
5.2. These areas of high stress become enodic, while the lower stress areas are cathodic
5.3. The stressed area will corrode quickly


