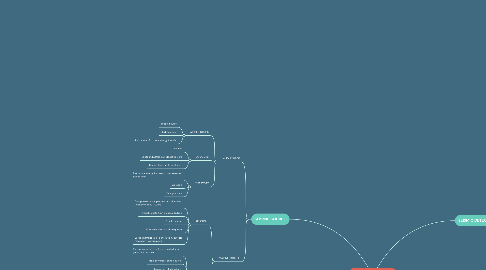
1. SEISMIC SOURCE
1.1. LAND SOURCE
1.1.1. WEIGHT DROPS
1.1.1.1. Impact source
1.1.1.2. Sledghammer
1.1.1.3. Hit on metal, for more energy transfer
1.1.2. EXPLOSIVE
1.1.2.1. Dynamite
1.1.2.2. Shotgun/buffalo gun donating cord
1.1.2.3. Use on land, soft, weathered
1.1.3. VIBRATORY
1.1.3.1. Propagate energy into earth over extended period time
1.1.3.2. Vibroseis
1.1.3.3. Thumper truck
1.2. MARINE SOURCE
1.2.1. AIR GUN
1.2.1.1. Compressed air is pimped into chamber - frequency of 10-100ohz
1.2.1.2. Through create high pressure bubble
1.2.1.3. Small chamber
1.2.1.4. Max resolution - high frequency
1.2.1.5. Large chamber, max penetration, but less resolution- low frequency
1.2.2. SPARKERS
1.2.2.1. Plasma sound source (pss) or called spark gap sound source
1.2.2.2. High powered sound source
1.2.2.3. Depend on electrical arc
1.2.2.4. Vaporize water between positively and negatively
1.2.2.5. It stores high volt charge
1.2.2.6. Release all stored energy in arc cross electrodes
1.2.2.7. Underwater pressure produce high pressure plasma and vapour bubble collapse and make loud sound
2. SEISMIC DETECTOR
2.1. LAND DETECTOR
2.1.1. GEOPHONES
2.1.1.1. Measure only single component of motion(verticle) earth act as low pass filter
2.1.1.2. Maximum amplitude will be at low frequency
2.1.2. SEISMOMETER
2.1.2.1. Similar to geophone but permanent housing use to detect earthquake
2.2. MARINE DETECTOR
2.2.1. HYDROPHONES
2.2.1.1. Detect change in pressure in water and piezoelectric element change into electric signal streamer, pressure sensor, compass, tail buoys fins & bird
2.2.2. OCEAN-BOTTOM SEISMOMETER(OBS)
2.2.2.1. Similar to seismometer but house in airtight, metal container that sink to sea. Limited= battery power, hard drive space
3. IMPORTANCE CONSIDERATION
3.1. Sampling Rate
3.2. Sampling Frequency
3.3. Trace length
3.4. Nyguist Frequency
3.5. Seismic Record
3.6. Analog
3.6.1. Limitatio- depend on capability of recording
3.6.2. Strip chart record
3.6.3. Magnetic tape
3.6.4. Digital
3.6.5. Analog to digital (a/d) converter
3.6.6. Sampling the signal in ms and reprent amplitude signal at that moment by number

