Paradigm
by mike adolph
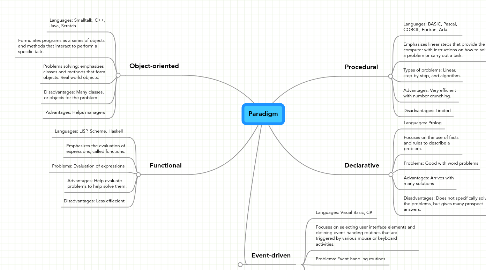
1. Object-oriented
1.1. Languages: Smalltalk, C++, Java, Scratch
1.2. Formulates programs as a series of objects and methods that interact to perform a specific task.
1.3. Problems solving: emphasizes classes and methods that form objects. Real world objects.
1.4. Disadvantages: Many classes, or objects for the problem.
1.5. Advantages: Helps managers
2. Functional
2.1. Languages: LISP, Scheme, Haskell
2.2. Emphasizes the evaluation of expressions, called functions.
2.3. Problems: Evaluation of expressions
2.4. Advantages: Help evaluate problems to help solve them.
2.5. Disadvantages: Less effiecient
3. Event-driven
3.1. Languages: Visual Basic, C#
3.2. Focuses on selecting user interface elements and defining event-handing routines that are triggered by various mouse or keyboard activities.
3.3. Problems: Event-handling routines.
3.4. Advantages: significantly reduce development time and simplify the entire programming process.
3.5. Disadvantages: Syntax errors
4. Procedural
4.1. Languages: BASIC, Pascal, COBOL, Fortran, Ada.
4.2. Emphasizes linear steps that provide the computer with instructions on how to solve a problem or carry out a task.
4.3. Types of problems: Linear, step-by-step, and algorithm.
4.4. Advantages: Very efficient with number crunching.
4.5. Disadvantages: Limited
5. Declarative
5.1. Languages: Prolog
5.2. Focuses on the use of facts and rules to describe a problem.
5.3. Problems: Good with word problems
5.4. Advantages: Arrives with many solutions
5.5. Disadvantages: Does not specifically solve the problems, but gives many prospect answers.


