Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD)
by Matthew Ciezki
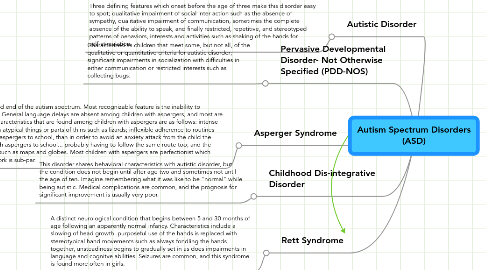
1. Autistic Disorder
1.1. Three defining features which onset before the age of three make this disorder easy to spot; qualitative impairment of social inter action such as the absence of sympathy, qualitative impairment of communication, sometimes the complete absence of the ability to speak, and finally restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behaviors, interests and activities such as shaking of the hands for self-stimulation.
2. Asperger Syndrome
2.1. This syndrome is found near the mild end of the autism spectrum. Most recognizable feature is the inability to understand how to socially interact. General language delays are absent among children with aspergers, and most are not intellectually disabled. Other characteristics that are found among children with aspergers are as follows: intense interest in a particular subject, often atypical things or parts of thins such as lizards; inflexible adherence to routines such as if mom takes the child with aspergers to school, than in order to avoid an anxiety attack from the child the mom must always take the child with aspergers to school... probably having to follow the same route too; and the wildly deep fascination with things such as maps and globes. Most children with aspergers are perfectionist which means that they always feel their work is sub-par.
3. Rett Syndrome
3.1. A distinct neurological condition that begins between 5 and 30 months of age following an apparently normal infancy. Characteristics include a slowing of head growth, purposeful use of the hands is replaced with stereotypical hand movements such as always fondling the hands together, unsteadiness begins to gradually set in as does impairments in language and cognitve abilities. Seizures are common, and this syndrome is found more often in girls.
4. Childhood Dis-integrative Disorder
4.1. This disorder shares behavioral characteristics with autistic disorder, but the condition does not begin until after age two and sometimes not until the age of ten. Imagine remembering what it was like to be "normal" while being autistic. Medical complications are common, and the prognosis for significant improvement is usually very poor.
5. Pervasive Developmental Disorder- Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS)
5.1. Characterized as children that meet some, but not all, of the qualitative or quantitative criteria for autistic disorder; significant impairments in socialization with difficulties in either communication or restricted interests such as collecting bugs.


