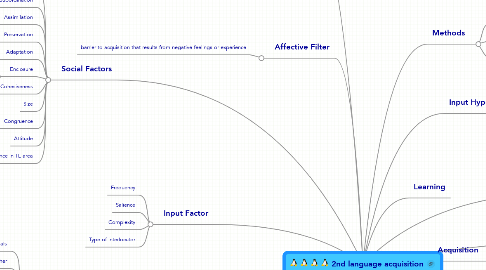
1. Affective Factors
1.1. Language Shock
1.1.1. fear of appearing comic
1.2. Culture Shock
1.2.1. anxiety resulting from the disorientation encoutered upon entering a new culture
1.3. Motivation
1.3.1. integrative motivation
1.3.1.1. meet with, talk to, find out about and become like speakers of the TL group
1.3.2. instrumental motivation
1.3.2.1. utilitarian reasons such as getting ahead in the occupation or gaining recognition
1.4. Ego-Permeability
2. Affective Filter
2.1. barrier to acquisition that results from negative feelings or experience
3. Social Factors
3.1. Dominance / Nondominance
3.2. Subordination
3.3. Assimilation
3.3.1. giving up own lifestyle and values and adopting those of TL group
3.3.1.1. maximises contact
3.4. Preservation
3.4.1. maintaining own lifestyle and values and rejecting those of TL group
3.4.1.1. creates social distance
3.5. Adaptation
3.5.1. adapting lifestyle and values of TL group but maitaining own lifestyle for intragroup use
3.5.1.1. varying degrees of contact with TL group
3.6. Enclosure
3.6.1. sharing churches, schools, clubs, recreational facilities, crafts, professions and trades
3.7. Cohesiveness
3.8. Size
3.9. Congruence
3.9.1. similarity between cultures
3.10. Attitude
3.11. Intended Length of Residence in TL area
4. Input Factor
4.1. Frequency
4.2. Salience
4.3. Complexity
4.4. Type of interlocutor
5. Instructional Factors
5.1. Goals
5.2. Teacher
5.3. Method
5.4. Text
5.5. Duration
5.6. Intensity
6. Communicative Competence
6.1. grammatical competence
6.2. sociolinguistic competence
6.3. strategic competence
7. Cognitive Factors
7.1. Cognitive Development
7.2. Cognitive Processes
7.2.1. imitation
7.2.2. analogy
7.2.3. generalisation
7.2.4. rote memorisation
7.3. Cognitive Style
7.3.1. field dependence
7.3.2. category width
7.3.3. cognitive interference
7.3.4. monitoring
