Chemical Reactions
por Miwka Mico
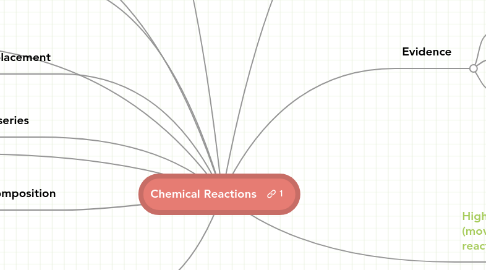

1. AB=(heat)> A+B
2. A + BX → AX + B
2.1. A and B are different metals
3. A DR reaction will only occur, if one the pairs of ions will combine and leave the solution. That means it forms a solid precipitate, a gas or water.
4. Occur based on reactivity series
5. Double Displacement
5.1. AB+CD => AD+BC
5.1.1. The cations and anions switch elements
5.2. 2 compounds to start 2 compounds produced
5.3. Nature of the product, determined by solubility table
6. Single Displacement
7. Synthesis
7.1. A+B=> AB
7.2. Combination of 2 reactants, only one product
8. Decomposition
8.1. Breaking down of a compound into its simple starting reactants (into elements)
9. Neutralization Reaction
9.1. Acid+Base=> Water+Salt
9.2. Ex//Brushing teeth with the use of toothpaste, toothpaste is an alkaline substance that neutralizes the acid formed from the decomposing food you ate all day that happened to get stuck to your teeth
10. Higher Temp, more kinetic energy (move faster), increase in the rate of reaction
11. Uses
11.1. Rearrangement of atoms (Chemical Reaction)
11.2. Separates Compounds
11.3. Obeys the Law of Mass Conservation
11.3.1. Balance Equations
11.3.1.1. Types and number of atoms are the same on each side of the equation
12. Evidence
12.1. Color Changes
12.2. Heat/ Light released/ absorbed
12.3. Formation of gas/ precipitate
12.3.1. Precipitate: does not dissolve, solid at room temp
