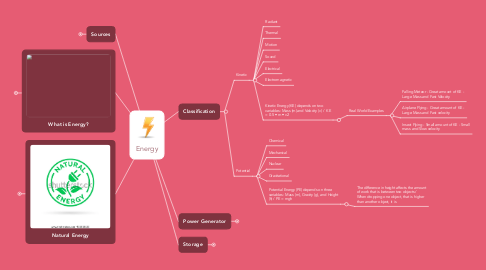
1. Classification
1.1. Kinetic
1.1.1. Radiant
1.1.2. Thermal
1.1.3. Motion
1.1.4. Sound
1.1.5. Electrical
1.1.6. Electromagnetic
1.1.7. Kinetic Energy (KE) depends on two variables: Mass (m) and Velocity (v) / KE = 0.5 • m • v2
1.1.7.1. Real World Examples
1.1.7.1.1. Falling Meteor - Great amount of KE - Large Mass and Fast Velocity
1.1.7.1.2. Airplane Flying - Great amount of KE - Large Mass and Fast velocity
1.1.7.1.3. Insect Flying - Small amount of KE - Small mass and Slow velocity
1.2. Potential
1.2.1. Chemical
1.2.2. Mechanical
1.2.3. Nuclear
1.2.4. Gravitational
1.2.5. Potential Energy (PE) depends on three variables: Mass (m), Gravity (g), and Height (h) / PE = mgh
1.2.5.1. The difference in height affects the amount of work that is between two objects / When dropping one object, that is higher than another object, it is
2. Sources
2.1. IT IS EVERYWHERE
2.2. Examples
2.2.1. Electric powered Devices
2.2.1.1. Phones
2.2.1.2. Laptop/PC
2.2.1.3. Headphones/Earphones
2.2.1.4. Mouse
2.2.1.5. Camera
2.2.2. Accesories
2.2.2.1. Battery
2.2.2.2. Wires
2.2.2.3. Clock/Watch
2.2.2.4. Charger
2.2.2.5. Projecter
3. What is Energy?
3.1. E = mc2
3.2. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change.
3.3. Energy is different from matter; matter is made of atoms, therefore Energy is not made of atoms.
3.4. Energy travels from an object to to another object while "working."
3.5. It cannot be created nor destroyed.
3.6. It comes in different forms: Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, Heat, Mechanical Energy, Light, Electrical and so much more.
4. Natural Energy
4.1. Wind
4.2. Sunlight
4.3. Geothermal
4.4. Fossil Fuels
4.4.1. Coal
4.4.2. Gas
4.4.3. Oil

