Past Continuous X Simple Past
저자: Ana Clara Flores da Cunha Marques
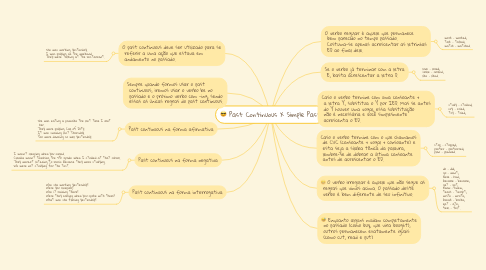
1. O past continuous deve ser utilizado para se referir a uma ação que estava em andamento no passado.
1.1. She was working yesterday. I was playing on the weekend. They were talking at the restaurant.
2. Sempre quando formos usar o past continuous, iremos usar o verbo be no passado e o próximo verbo com -ing, sendo essas as únicas regras do past continuous.
3. Past continuous na forma afirmativa
3.1. She was eating a pancake the last time I met her. They were playing Call of Duty. It was snowing last Thursday. You were dancing so well yesterday.
4. Past continuous na forma negativa
4.1. I wasn’t sleeping when you called. Claudia wasn’t teaching the 5th grade when I studied at that school. They weren’t listening to music because they were studying. We were not studying for the test.
5. Past continuous na forma interrogativa
5.1. Was she working yesterday? Were you sleeping? Was it raining there? Were they coming when you spoke with them? What was she filming yesterday?
6. O verbo regular é aquele que permanece bem parecido no tempo passado. Costuma-se apenas acrescentar as letrinhas ED ao final dele.
6.1. work – worked; talk – talked; watch – watched.
7. Se o verbo já terminar com a letra E, basta acrescentar a letra D.
7.1. love – loved; smile – smiled; like – liked.
8. Caso o verbo termine com uma consoante + a letra Y, substitua o Y por IED. Mas se antes do Y houver uma vogal, essa substituição não é necessária e você simplesmente acrescenta o ED.
8.1. study – studied; cry – cried; try – tried;
9. Caso o verbo termine com o que chamamos de CVC (consoante + vogal + consoante) e esta seja a sílaba tônica da palavra, lembre-se de dobrar a última consoante antes de acrescentar o ED.
9.1. stop – stopped; prefer – preferred; plan – planned.
10. O verbo irregular é aquele que não segue as regras que vimos acima. O passado deste verbo é bem diferente de seu infinitivo.
10.1. do – did; go – went; have – had; become – became; get – got; know – knew; teach – taught; write – wrote; break – broke; eat – ate; feel – felt.
11. Enquanto alguns mudam completamente no passado (como buy, que vira bought), outros permanecem exatamente iguais (como cut, read e put)


