PHI premium rate increase
저자: dexy dog
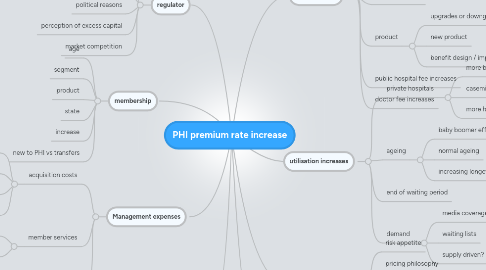

1. Management expenses
1.1. acquisition costs
1.1.1. commission
1.1.2. marketing
1.1.3. postage
1.1.4. labour costs
1.2. member services
1.2.1. telephones
1.2.2. IT costs
1.3. indirect expenses
1.3.1. corporate overhead
1.3.2. other eg risk margins
2. membership
2.1. age
2.2. segment
2.3. product
2.4. state
2.5. increase
2.6. new to PHI vs transfers
3. regulator
3.1. historical increases
3.2. accuracy of past projections
3.3. political reasons
3.4. perception of excess capital
3.5. market competition
4. actuarial matters
4.1. price relativities
4.2. allowance for waiting periods
5. cost increases
5.1. private hospital cost increases
5.1.1. same day
5.1.2. overnight
5.1.3. casemix
5.2. ageing
5.2.1. risk equalisation
5.2.2. casemix
5.3. new technology
5.4. product
5.4.1. upgrades or downgrades
5.4.2. new product
5.4.3. benefit design / improvement
5.5. public hospital fee increases
5.6. doctor fee increases
6. utilisation increases
6.1. private hospitals
6.1.1. more beds
6.1.1.1. demand driven?
6.1.2. casemix
6.1.3. more hospitals
6.2. ageing
6.2.1. baby boomer effect
6.2.2. normal ageing
6.2.3. increasing longevity
6.3. end of waiting period
6.4. demand
6.4.1. media coverage of public hospitals
6.4.2. waiting lists
6.4.3. supply driven?
