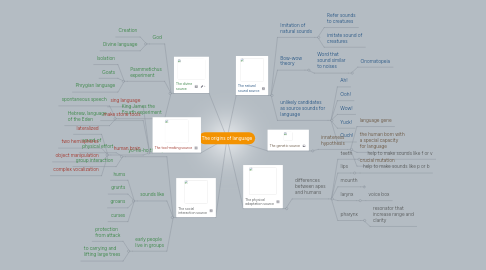
1. The divine source
1.1. God
1.1.1. Creation
1.1.2. Divine language
1.2. Psammetichus experiment
1.2.1. Isolation
1.2.2. Goats
1.2.3. Phrygian language
1.3. King James the Fourth experiment
1.3.1. spontaneous speech
1.3.2. Hebrew, language of the Eden
2. The social interaction source
2.1. yo-he-ho theory
2.1.1. sound of physical effort
2.1.2. group interaction
2.2. sounds like
2.2.1. hums
2.2.2. grunts
2.2.3. groans
2.2.4. curses
2.3. early people live in groups
2.3.1. protection from attack
2.3.2. to carrying and lifting large trees
3. The tool-making source
3.1. sing language
3.2. make stone tools
3.3. human brain
3.3.1. lateralized
3.3.2. two hemispheres
3.3.3. object manipulation
3.3.4. complex vocalization
4. The natural sound source
4.1. Imitation of natural sounds
4.1.1. Refer sounds to creatures
4.1.2. imitate sound of creatures
4.2. Bow-wow theory
4.2.1. Word that sound similar to noises
4.2.1.1. Onomatopeia
4.3. unlikely candidates as source sounds for language
4.3.1. Ah!
4.3.2. Ooh!
4.3.3. Wow!
4.3.4. Yuck!
4.3.5. Ouch!
5. The physical adaptation source
5.1. differences between apes and humans
5.1.1. teeth
5.1.1.1. help to make sounds like f or v
5.1.2. lips
5.1.2.1. help to make sounds like p or b
5.1.3. mounth
5.1.3.1. a tongue which can be used to shape sounds
5.1.4. larynx
5.1.4.1. voice box
5.1.5. pharynx
5.1.5.1. resonator that increase range and clarity
6. The genetic source
6.1. innateness hypothesis
6.1.1. language gene
6.1.2. the human born with a special capacity for language
6.1.3. crucial mutation
