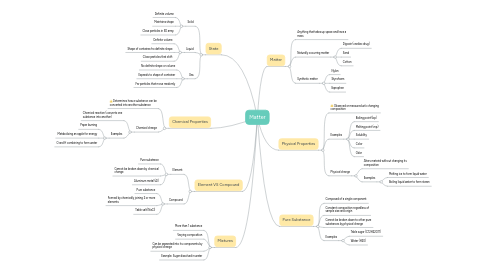
1. State
1.1. Solid
1.1.1. Definite volume
1.1.2. Maintains shape
1.1.3. Close particles in 3D array
1.2. Liquid
1.2.1. Definite volume
1.2.2. Shape of container/no definite shape
1.2.3. Close particles that shift
1.3. Gas
1.3.1. No definite shape or volume
1.3.2. Expands to shape of container
1.3.3. Far particles that move randomly
2. Chemical Properties
2.1. Determines how a substance can be converted into another substance
2.2. Chemical change
2.2.1. Chemical reaction (converts one substance into another)
2.2.2. Examples
2.2.2.1. Paper burning
2.2.2.2. Metabolizing an apple for energy
2.2.2.3. O and H combining to form water
3. Mixtures
3.1. More than 1 substance
3.2. Varying composition
3.3. Can be separated into its components by physical change
3.4. Example: Sugar dissolved in water
4. Element VS Compound
4.1. Element
4.1.1. Pure substance
4.1.2. Cannot be broken down by chemical change
4.1.3. Aluminum metal (Al)
4.2. Compound
4.2.1. Pure substance
4.2.2. Formed by chemically joining 2 or more elements
4.2.3. Table salt (NaCl)
5. Matter
5.1. Anything that takes up space and have a mass
5.2. Naturally occurring matter
5.2.1. Digoxin (cardiac drug)
5.2.2. Sand
5.2.3. Cotton
5.3. Synthetic matter
5.3.1. Nylon
5.3.2. Styrofoam
5.3.3. Ibprophen
6. Physical Properties
6.1. Observed or measured w/o changing composition
6.2. Examples
6.2.1. Boiling point (bp)
6.2.2. Melting point (mp)
6.2.3. Solubility
6.2.4. Color
6.2.5. Odor
6.3. Physical change
6.3.1. Alters material without changing its composition
6.3.2. Examples
6.3.2.1. Melting ice to form liquid water
6.3.2.2. Boiling liquid water to form steam
7. Pure Substance
7.1. Composed of a single component
7.2. Constant composition regardless of sample size and origin
7.3. Cannot be broken down to other pure substances by physical change
7.4. Examples
7.4.1. Table sugar (C12H22O11)
7.4.2. Water (H20)

