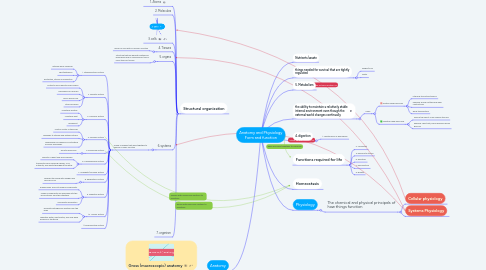
1. Structural organization
1.1. 1. Atoms
1.2. 2. Molecules
1.3. 3. cells
1.4. 4. Tissues
1.4.1. group of cells with a common function
1.5. 5. organs
1.5.1. Structure that has definite anatomical boundaries and is comprised of two or more types of tissues
1.6. 6. systems
1.6.1. Group of organs that work together to perform a basic function
1.6.1.1. 1. Integumentary System
1.6.1.1.1. external body covering
1.6.1.1.2. skin/epithelium
1.6.1.1.3. protection, vitamin D production
1.6.1.2. 2. Skeletal System
1.6.1.2.1. protects and supports body organs
1.6.1.2.2. framework for muscles
1.6.1.2.3. forms blood cells
1.6.1.2.4. stores minerals
1.6.1.3. 3. Muscular system
1.6.1.3.1. maintains posture
1.6.1.3.2. Maintains heat
1.6.1.3.3. movement
1.6.1.4. 4. Nervous system
1.6.1.4.1. control center of the body
1.6.1.4.2. responds to internal and external stimuli
1.6.1.4.3. responsible for behavior by activating muscles and glands
1.6.1.5. 5. Endocrine system
1.6.1.5.1. secrete hormones
1.6.1.6. 6. Cardiovascular system
1.6.1.6.1. consists of heart and blood vessels
1.6.1.6.2. transports blood carrying oxygen, CO2, nutrients, and waste throughout the body
1.6.1.7. 7. Lymphatic/Immune system
1.6.1.8. 8. Respiratory System
1.6.1.8.1. supplies the blood with oxygen and removes CO2
1.6.1.9. 9. Digestive system
1.6.1.9.1. breaks down food into usable components
1.6.1.9.2. Usable components are absorbed into the blood stream from the intestines
1.6.1.9.3. solid waste elimination
1.6.1.10. 10. Urinary system
1.6.1.10.1. eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body
1.6.1.10.2. regulates water, electrolytes, and acid-base balance of the blood
1.6.1.11. 11. Reproductive system
1.7. 7. organism
2. Anatomy
2.1. Gross (macroscopic) anatomy
2.2. Microscopic anatomy
2.2.1. cytology
2.2.1.1. cellular anatomy
2.2.2. Histology
2.2.2.1. tissue anatomy
3. Nutrients/waste
4. things needed for survival that are tightly regulated
4.1. oxygen/CO2
4.2. Water
5. 5. Metabolism
6. the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment even though the external world changes continually
6.1. How?
6.1.1. Positive feed back loop
6.1.1.1. intensify the initial stimulus
6.1.1.2. example: blood clotting and labor contractions
6.1.1.3. Body temperature
6.1.2. Negative feed back loop
6.1.2.1. reduce the effect of an original stimulus
6.1.2.2. example: heart rate, blood pressure blood glucose
7. 4. digestion
7.1. 1. Maintenance of Boundaries
8. Functions required for life
8.1. 2. Movement
8.2. 3. respond to stimuli
8.3. 6. Excretion
8.4. 7. reproduction
8.5. 9. growth
9. Homeostasis
10. Physiology
10.1. The chemical and physical principals of how things function
10.1.1. Cellular physiology
10.1.2. Systems Physiology
