Indo-European Languages.
作者:Desiree Serrano
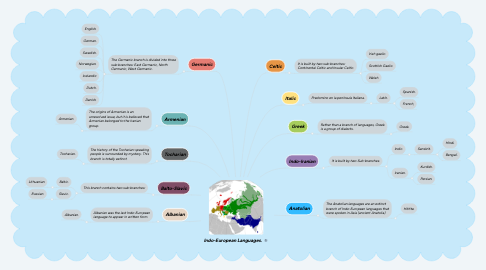

1. Germanic
1.1. The Germanic branch is divided into three sub-branches: East Germanic, North Germanic, West Germanic.
1.1.1. English.
1.1.2. German.
1.1.3. Swedish.
1.1.4. Norwegian.
1.1.5. Icelandic
1.1.6. Dutch.
1.1.7. Danish.
2. Armenian
2.1. The origins of Armenian is an unresolved issue, but it is believed that Armenian belonged to the Iranian group.
2.1.1. Armenian.
3. Tocharian
3.1. The history of the Tocharian-speaking people is surrounded by mystery. This branch is totally extinct.
3.1.1. Tocharian.
4. Balto-Slavic
4.1. This branch contains two sub-branches:
4.1.1. Baltic.
4.1.1.1. Lithuanian
4.1.2. Slavic.
4.1.2.1. Russian.
5. Albanian
5.1. Albanian was the last Indo-European language to appear in written form.
5.1.1. Albanian.
6. Anatolian
6.1. The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Asia (ancient Anatolia).
6.1.1. Hittite.
7. Indo-Iranian
7.1. It is built by two Sub-branches.
7.1.1. Indic.
7.1.1.1. Sanskrit.
7.1.1.1.1. Hindi.
7.1.1.1.2. Bengali.
7.1.2. Iranian.
7.1.2.1. Kurdish.
7.1.2.2. Persian.
8. Greek
8.1. Rather than a branch of languages, Greek is a group of dialects.
8.1.1. Greek.
9. Italic
9.1. Predomino en la península Italiana.
9.1.1. Latín.
9.1.1.1. Spanish.
9.1.1.2. French,
10. Celtic
10.1. It is built by two sub-branches: Continental Celtic and Insular Celtic.
10.1.1. Irish gaelic.
10.1.2. Scottish Gaelic.
10.1.3. Welsh.
