Reliability
作者:Paul Horrigan
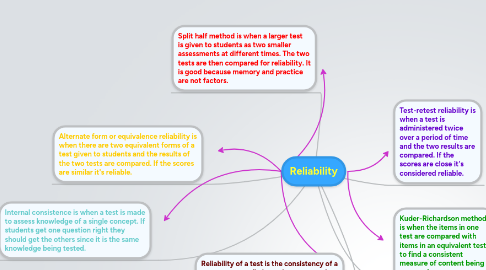
1. Reliability of a test is the consistency of a test to repeatedly have the same results over many administered testing times.
1.1. New node
2. Alternate form or equivalence reliability is when there are two equivalent forms of a test given to students and the results of the two tests are compared. If the scores are similar it's reliable.
3. Internal consistence is when a test is made to assess knowledge of a single concept. If students get one question right they should get the others since it is the same knowledge being tested.
4. Split half method is when a larger test is given to students as two smaller assessments at different times. The two tests are then compared for reliability. It is good because memory and practice are not factors.
5. Test-retest reliability is when a test is administered twice over a period of time and the two results are compared. If the scores are close it's considered reliable.
6. Kuder-Richardson methods is when the items in one test are compared with items in an equivalent test to find a consistent measure of content being assessed.


