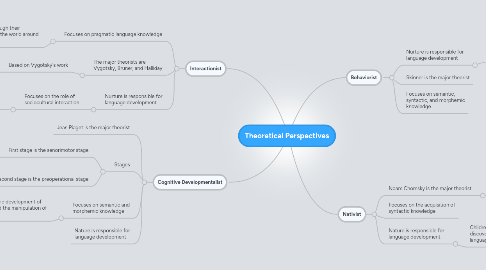
1. Cognitive Developmentalist
1.1. Jean Piaget is the major theorist
1.2. Stages
1.2.1. First stage is the senorimotor stage
1.2.1.1. Children understand object permanence
1.2.1.1.1. Children start to use words and symbols to represent objects and actions.
1.2.2. Second stage is the preoperational stage
1.2.2.1. Starts around 2 and goes to about 7 years old.
1.2.2.1.1. Children begin to "represent the world with words, images, and drawings" (Otto, 2010).
1.3. Focuses on semantic and morphemic knowledge
1.3.1. Focuses on the development of schemata and the manipulation of symbols.
1.4. Nature is responsible for language development
2. Interactionist
2.1. Focuses on pragmatic language knowledge
2.1.1. "Children acquire language through their attempts to communicate with the world around them" (Otto, 2010).
2.2. The major theorists are Vygotsky, Bruner, and Halliday
2.2.1. Based on Vygotsky's work
2.2.1.1. Zone of proximal development
2.2.1.2. Developmental level
2.3. Nurture is responsible for language development
2.3.1. Focuses on the role of sociocultural interaction
2.3.1.1. The language acquisition support system (LASS)
2.3.1.1.1. Cambourne's eight conditions: immersion, demonstration, engagement, expectations, responsibilitiy, approximations, employment, and response
3. Behaviorist
3.1. Nurture is responsible for language development
3.1.1. Learning is based on the environment
3.1.1.1. operant conditioning and imitative speech helps language development
3.2. Skinner is the major theorist
3.3. Focuses on semantic, syntactic, and morphemic knowledge
4. Nativist
4.1. Noam Chomsky is the major theorist
4.1.1. Universal grammar
4.1.1.1. innate property of the human mind
4.2. Focuses on the acquisition of syntactic knowledge
4.3. Nature is responsible for language development
4.3.1. Children learn language by discovering the structure of their language
4.3.1.1. language acquisition device (LAD)
