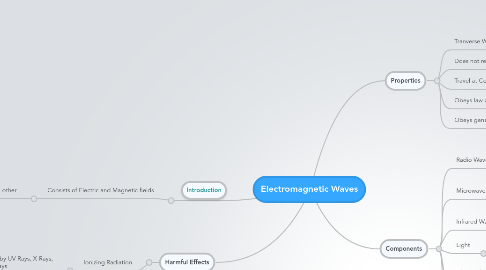
1. Harmful Effects
1.1. Ionizing Radiation
1.1.1. Produced by UV Rays, X-Rays, Gamma Rays
1.1.1.1. causes electrons to gain energy and escape from the atoms
1.1.1.1.1. Atoms become charged and unstable
2. Introduction
2.1. Consists of Electric and Magnetic fields
2.1.1. Oscillating perpendicularly to each other
3. Properties
3.1. Tranverse Waves
3.2. Does not require medium to propagate
3.3. Travel at Constant Speed
3.3.1. 3.0 x 10^8 m/s
3.4. Obeys law of Reflection and Refraction
3.5. Obeys general wave equation
3.5.1. c = f x wavelength
4. Components
4.1. Radio Waves
4.1.1. Source: Produced by Electronic Oscillating in Electrical Circuits
4.1.1.1. Uses: Radio and TV Transmission
4.2. Microwaves
4.2.1. Source: Special Electronic Devices e.g. Klystron
4.2.1.1. Uses: Heat up food by giving water molecules energy in the food which in turns produces heat energy, Satallite Communication
4.3. Infrared Waves
4.3.1. Source: Hot Objects
4.3.1.1. Uses: Infrared Detector, converts Infrared into Images
4.4. Light
4.4.1. Uses: To be able to see
4.5. Ultra-Violet Rays
4.5.1. Source: Sunlight
4.5.1.1. Uses: Produce Suntan, Kills Bacteria, Check for counterfeit notes
4.6. X-Rays
4.6.1. Source: By firing high speed electrons at metal target
4.6.1.1. Uses: Produce image of bone structure
4.7. Gamma Rays
4.7.1. Highest Frequency
4.7.1.1. Source: Emitted by the nucleus of radioactive atoms
4.7.1.1.1. Uses: Sterilise Medical Instruments, Kill Cancerous Cells
