1. Lesson 1
1.1. Uniformitarianism
1.1.1. the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes.
1.2. Absolute Age
1.2.1. the true age of a layer of rocks or fossils
1.3. Relative Age Dating
1.3.1. using the rock layers and fossils to build a record of geologic history
1.4. Sediment
1.4.1. rocks that are broken by weathering into smaller pieces
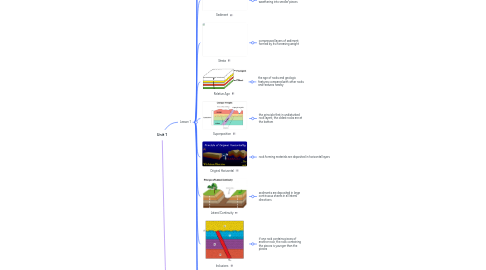
1.5. Strata
1.5.1. compressed layers of sediment formed by its increasing weight
1.6. Relative Age
1.6.1. the age of rocks and geologic features compared with other rocks and features nearby
1.7. Superposition
1.7.1. the principle that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are at the bottom
1.8. Original Horizontal
1.8.1. rock forming materials are deposited in horizontal layers
1.9. Lateral Continuity
1.9.1. sediments are deposited in large continuous sheets in all lateral directions
1.10. Inclusions
1.10.1. if one rock contains pieces of another rock, the rock containing the pieces is younger than the pieces
1.11. Cross cutting relationships
1.11.1. if one geologic features cuts across another feature, the feature that it cuts across is older
1.12. The Fossil Record
1.12.1. Older rocks contain simple life forms. Younger rocks contain more complex life forms. Empty rock layers without fossils meant life had disappeared during that time. Fossils and the rocks they are within can be used to determine what the environment of an area was like.
1.13. Mass Extinctions
1.13.1. times when many species on Earth died or became extinct in a short period of time
2. Lesson 2
2.1. Unconformaties
2.1.1. When rock has eroded away, producing breaks, or gaps, in the rock record. This is when new sediment is deposited on top of old, eroded rock layers
