1. Google Search Appliance (GSA)
1.1. Purpose
1.1.1. To Harness and leverage Google's superior search technology in a box, respecting all current privacy/confidentiality rules, searching both structured and unstructured data, indexing the SQL databases and over 220 different document formats, while preserving Google's speed and accuracy. The most relevant search results are then used by the ITA dashboard for case management or aggregate data analyses.
1.2. Features & Benefits
1.2.1. Indexes Virtually Any Document or SQL Db
1.2.1.1. Works non-intrusively alongside current legacy systems
1.2.1.2. Retrieves data from APIs or any URL-driven interface
1.2.1.3. Communicates with SQL Db's via a connector (jdbc)
1.2.1.4. Recognizes over 220 file formats in more than 70 different languages
1.2.1.5. All-in-one solution that treats both structured and unstructured data equally
1.2.2. Respects Current Privacy & Confidentiality Restrictions
1.2.2.1. Configurable to abide by the client's current privacy & confidentiality rules
1.2.2.2. Configures user access down to a table's row, column, or single cell
1.2.3. Meets Gov't Security Requirements
1.2.3.1. Google is the first provider to complete FISMA certification for a multi-tenant cloud application.
1.2.3.2. Google Cloud Platform supports HIPAA Covered Entities
1.2.4. Cloud & Private Network Deployments
1.2.4.1. GSA supports both environments
1.2.5. Easy to Set-Up & Use
1.2.5.1. No programming required. Completely configurable via browser
1.2.5.2. Out-of-the-box, provides a universal search bar that returns XML formatted results
1.2.6. Extremely Cost-Effective
1.2.6.1. License fees are calculated by the number of documents
1.2.6.2. A fraction of the cost of legacy systems
1.2.7. Utilizes Google's Unique Web Search Technology
1.2.7.1. Leverages Google's proprietary algorithms that are unmatched in accuracy and relevance
1.2.7.2. Uses built-in spelling alternatives and probablistic analyses essential for both unstructured and structured data
1.2.7.3. Search results are returned almost instantly, just as they are for web searches
1.2.8. Offers the advanced features of Google Search
1.2.8.1. Limit scope of the search, build complex search expressions, choose the languages, etc.
1.3. DHH Cross-Connect
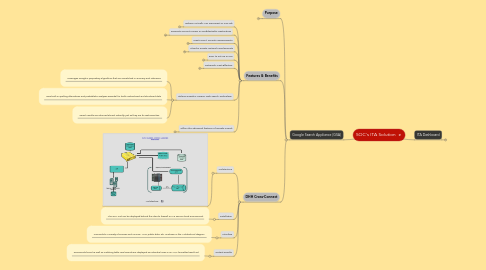
1.3.1. Architecture
1.3.1.1. Architecture
1.3.2. Installation
1.3.2.1. The GSA unit can be deployed behind the client's firewall or in a secure cloud environment.
1.3.3. Interface
1.3.3.1. Connects to a variety of sources such as SQL, APIs, public data, etc. as shown in the Architectural diagram
1.3.4. Output Results
1.3.4.1. Documents found as well as matching table row/records are displayed as individual rows in an XML-formatted result set
2. ITA Dashboard
2.1. Purpose
2.1.1. Act as a front-end to Google Search Appliance, providing an intuitive GUI which allows the user to search and interact with inter-agency data in a comprehensive and integrated way
2.2. Core Components
2.2.1. Search Interface
2.2.1.1. Universal Search Bar
2.2.1.1.1. The familiar Google search bar where data is entered in free-form style and GSA searches through either all its fields or just those configured.
2.2.1.2. Template Search
2.2.1.2.1. Select any record from a dataset or search result and click to submit all the case details to a new search which should return more focused results relating specifically to that client.
2.2.1.3. Data Fields Search
2.2.1.3.1. Traditional, structured database query that specifies the values for each field of interest being searched within the dataset
2.2.1.4. Optimizations
2.2.1.4.1. User can choose which datasets or agencies to include in the search, as well as how similar the "fuzzy" field value comparisons need to be in order to "match."
2.2.2. Identity Matching
2.2.2.1. Technology
2.2.2.1.1. Fuzzy Field Comparisons
2.2.2.1.2. Fuzzy Record Comparisons
2.2.2.1.3. Data Cleansing,Standardization, & Validation
2.2.2.2. How ITA integrates it
2.2.2.2.1. Challenge
2.2.2.2.2. Solution
2.2.3. Data Visualization
2.2.3.1. Maps
2.2.3.1.1. Google Maps is still the most cost-effective, feature-rich, and easy-to-use geospatial package as a whole, providing such popular features as "Street View" and the points of interest database called "Places."
2.2.3.2. Charts
2.2.3.2.1. Aside from the standard graphs and charts, Google also offers some unique, animated graphs like its "network graph", Regardless of the vendor, however, all charts will be rendered and updated in real-time and in sync with the underlying data.
2.2.3.3. Grids
2.2.3.3.1. Much of the data will be presented through the Data Grid and Pivot Grid structures because of their built-in features that allow the user to filter, sort, group, summarize, and cross-compare data very easily.
2.2.4. Monitoring & Alerts
2.2.4.1. Trigger Criteria
2.2.4.1.1. Drag-and-Drop GUI
2.2.4.1.2. Custom Script option
2.2.4.2. Actions
2.2.4.2.1. Communication
2.2.4.2.2. Workflow and Data Updates
2.2.4.2.3. Analytics & Reporting
2.2.5. Machine Learning & Predictive Analytics
2.2.5.1. Google's Prediction API
2.2.5.1.1. ITA can upload all case history data including alerts, which Google will train with using its Prediction API service. Then given any new case history, the APIs can "predict" the value of any column in the data table that we select.
2.2.5.2. Self-analyzing system
2.2.5.2.1. Using AI technology, such as neural nets, along with more traditional statistics, we can examine our own data for patterns or make predictions based on neural network output or Prediction APIs like Google's.

