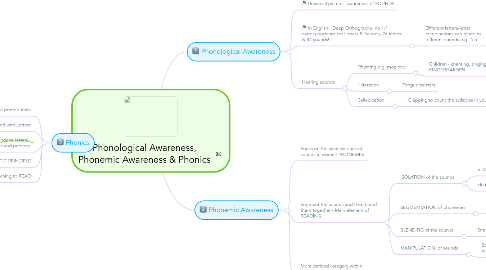
1. Phonics
1.1. Sounds in the printed texts
1.2. Sounds represented with Letters
1.3. Mapping sounds to letters - learn the rules and patterns
1.4. ALPHABETIC PRINCIPLE
1.5. Main step in the process of learning to READ
2. Phonological Awareness
2.1. Universal picture - awareness of SOUNDS
2.2. In English - Deep Orthography: no 1:1 correspondence for Letters & Sounds, 26 letters & 44 sounds!
2.2.1. Different letters/letter combinations can relate to different sounds e.g. "ch"
2.2.1.1. CHair
2.2.1.2. CHristmas
2.2.1.3. maCHine
2.3. Hearing sounds
2.3.1. Rhyming e.g. mop-top
2.3.1.1. Children - chanting, singing in KINDERGARDEN
2.3.2. Illiteration
2.3.2.1. Tongue twisters
2.3.3. Syllabication
2.3.3.1. Clapping to count the syllables in your name
3. Phonemic Awareness
3.1. Focus on the smallest units of sounds in words - PHONEMES
3.2. Segment the sounds and then blend them together - Main element of READING
3.2.1. ISOLATION of the sounds
3.2.1.1. in KINDERGARDEN - pictures, words
3.2.1.2. do it with initial, medial or final sounds
3.2.2. SEGMENTATION of phonemes
3.2.2.1. Counting the different sounds
3.2.2.1.1. e.g. C-A-T (3 phonemes)
3.2.2.1.2. e.g. SH-EE-P (3 phonemes)
3.2.3. BLENDING of the sounds
3.2.3.1. Stretch the word out and then put it together
3.2.3.1.1. e.g. "i"+"t" (they say "it")
3.2.4. MANIPULATION of sounds
3.2.4.1. Stretch the word out and then replace a sound with another one
3.2.4.1.1. e.g. "chair" - take away the "ch" and replace it with a "f" - "fair"

