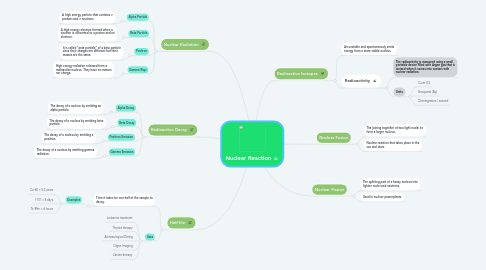
1. Nuclear Radiation
1.1. Alpha Particle
1.1.1. A high energy particle that contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
1.2. Beta Particle
1.2.1. A high energy electron formed when a neutron is converted to a proton and an electron.
1.3. Positron
1.3.1. It is called "ante particle" of a beta particle since their charges are different but their masses are the same.
1.4. Gamma Rays
1.4.1. High energy radiation released from a radioactive nucleus. They have no masses nor charge.
2. Radioactive Decay
2.1. Alpha Decay
2.1.1. The decay of a nucleus by emitting an alpha particle.
2.2. Beta Decay
2.2.1. The decay of a nucleus by emitting beta particle.
2.3. Positron Emission
2.3.1. The decay of a nucleus by emitting a positron.
2.4. Gamma Emission
2.4.1. The decay of a nucleus by emitting gamma radiation.
3. Half-life
3.1. Time it takes for one-half of the sample to decay.
3.1.1. Examples
3.1.1.1. Co-60 = 5.3 years
3.1.1.2. I-131 = 8 days
3.1.1.3. Tc-99m = 6 hours
3.2. Uses
3.2.1. Leukemia treatment
3.2.2. Thyroid therapy
3.2.3. Archaeological Dating
3.2.4. Organ Imaging
3.2.5. Cancer therapy
4. Radioactive Isotopes
4.1. An unstable and spontaneously emits energy from a more stable nucleus.
4.2. Radioactivity
4.2.1. The radioactivity is measured using a small portable device filled with Argon gas that is ionized when it comes into contact with nuclear radiation.
4.2.2. Units
4.2.2.1. Cuire (Ci)
4.2.2.2. Becquerel (Bq)
4.2.2.3. Disintegration / second

