1. Adjectives
1.1. Adjective kept more distinctive endings than the nouns
2. Passive
2.1. Passive and past perfect were formed by the verbs 'was' or 'become' + p.p
2.2. In OE , the passive could only be formed with verbs which took an object in the occusative case , rather than in dative and gentive
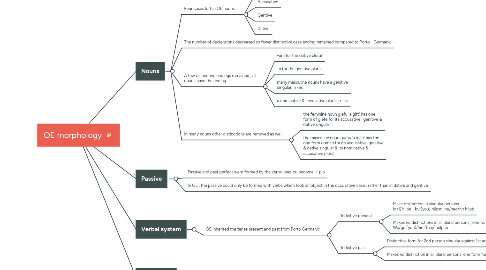
3. Nouns
3.1. Four cases left in OE nouns :
3.1.1. Nominative
3.1.2. Accusative
3.1.3. Gentive
3.1.4. Dative
3.2. The number of declensions decreased so fewer distinctive case ending remained compared to Porto - Germanic
3.3. A few distinctive endings remained , all nouns have the ending
3.3.1. -um for the dative plural
3.3.2. -a for the genitive plural
3.3.3. many masculine nouns have a genitive singular in -es
3.3.4. a nominative & accusative plural in -as
3.4. In many nouns other distinctions are removed as well
3.4.1. the feminine noun giefu 'a gift' has one form of giefe for its accusative , genitive & dative singular
3.4.2. the masculine noun guma 'a man' has the one form guman for its accusative, genitive & dative singular & its nominative & accusative plural
4. Verbal system
4.1. OE inherited the tense present and past from Porto Germanic
4.1.1. Indictive present
4.1.1.1. Make distinction in singular persons ic (I) hilpe - bu (you) hilpst- he/heo/hit hilpb
4.1.1.2. Makes no distinctions in all plural persons , one form for all We/ge (you)/hie (they)helpab
4.1.2. Indictive past
4.1.2.1. Distinctive form for 2nd person singular against 1st and 3rd person singular
4.1.2.2. Makes no distinction in all plural persons, one form for all
