The Blood System
af Charlette Yip
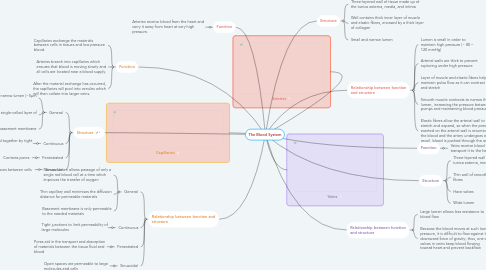
1. Relationship between function and structure
1.1. General
1.1.1. Narrow lumen allows passage of only a single red blood cell at a time which improves the transfer of oxygen
1.1.2. Thin capillary wall minimises the diffusion distance for permeable materials
1.1.3. Basement membrane is only permeable to the needed materials
1.2. Continuous
1.2.1. Tight junctions to limit permeability of large molecules
1.3. Fenestrated
1.3.1. Pores aid in the transport and absorption of materials between the tissue fluid and blood
1.4. Sinusoidal
1.4.1. Open spaces are permeable to large molecules and cells
2. Structure
2.1. General
2.1.1. Small diameter and narrow lumen (~5µm wide)
2.1.2. Wall is made of a single-celled layer of endothelium
2.1.3. Surrounded by a basement membrane
2.2. Continuous
2.2.1. Endothelial cells are held together by tight junctions
2.3. Fenestrated
2.3.1. Contains pores
2.4. Sinusoidal
2.4.1. Has open spaces between cells
3. Function
3.1. Capillaries exchange the materials between cells in tissues and low pressure blood.
3.2. Arteries branch into capillaries which ensures that blood is moving slowly and all cells are located near a blood supply.
3.3. After the material exchange has occurred, the capillaries will pool into venules which will then collate into larger veins.
4. Function
4.1. Arteries receive blood from the heart and carry it away from heart at very high pressure.
5. Arteries
6. Capillaries
7. Relationship between function and structure
7.1. Lumen is small in order to maintain high pressure (~ 80 – 120 mmHg)
7.2. Arterial walls are thick to prevent rupturing under high pressure
7.3. Layer of muscle and elastic fibres helps maintain pulse flow as it can contract and stretch
7.4. Smooth muscle contracts to narrow the lumen, increasing the pressure between pumps and maintaining blood pressure
7.5. Elastic fibres allow the arterial wall to stretch and expand, so when the pressure exerted on the arterial wall is returned to the blood and the artery undergoes elastic recoil, blood is pushed through the artery
8. Structure
8.1. Three-layered wall of tissue made up of the tunica externa, media, and intima
8.2. Wall contains thick inner layer of muscle and elastic fibres, encased by a thick layer of collagen
8.3. Small and narrow lumen
9. Veins
10. Function
10.1. Veins receive blood from capillaries and transport it to the heart at low pressure.
11. Structure
11.1. Three-layered wall of tissue made up of the tunica externa, media, and intima
11.2. Thin wall of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
11.3. Have valves
11.4. Wide lumen
12. Relationship between function and structure
12.1. Large lumen allows less resistance to blood flow
12.2. Because the blood moves at such low pressure, it is difficult to flow against the downward force of gravity; thus, one-way valves in veins keep blood flowing toward heart and prevent backflow

