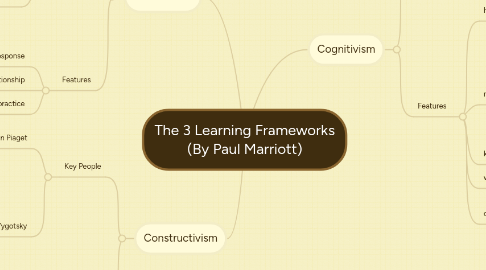
1. Behaviorism
1.1. Key People
1.1.1. E.L. Thorndike
1.1.1.1. Stimulus-Response Theory
1.1.1.2. Stimuli & Responses from learning
1.1.1.3. Law of Effect
1.1.2. B.F. Skinner
1.1.2.1. Reward & Reinforcement
1.1.2.1.1. +ve
1.1.2.1.2. -ve
1.1.2.2. Skinner Box Test
1.1.2.3. Stimulus Response Reinforcement Theory
1.2. Features
1.2.1. Learning through stimulus & response
1.2.2. cause & effect relationship
1.2.3. drill & practice
2. Constructivism
2.1. Key People
2.1.1. Jean Piaget
2.1.1.1. Theory of knowing
2.1.1.2. Knowledge mentally constructed
2.1.1.3. Environment Interaction
2.1.1.4. Epistemology
2.1.1.5. Cognitive-developmental theories
2.1.2. L.S. Vygotsky
2.1.2.1. Culture for cognitive development
2.1.2.2. Knowledge gained through mediation or social activity
2.2. Features
2.2.1. Learners construct own knowledge
2.2.1.1. assimilation
2.2.1.2. accommodation
2.2.1.3. discovery
2.2.2. Existing knowledge builds new knowledge
2.2.3. ideas
2.2.3.1. collect
2.2.3.2. use
3. Cognitivism
3.1. Key People
3.1.1. Jean Piaget
3.1.1.1. cognitive development theory
3.1.2. L.S. Vygotsky
3.1.2.1. Socio-cultural factors in education
3.1.2.2. Teaching restructured to support student self-learning
3.1.2.3. Inter-relationship of language development & thought
3.2. Features
3.2.1. human brain memory
3.2.1.1. short term
3.2.1.2. long term
3.2.1.3. working
3.2.2. mental processes
3.2.2.1. think
3.2.2.2. learn knowledge
3.2.2.3. perceive
3.2.2.4. remember
3.2.3. knowledge transfer
3.2.4. ways of thinking
3.2.5. discovery learning
3.2.5.1. relation of knowledge
3.2.5.2. importance of learning processes
