Uniform Circular Motion
by Kathryn Burns
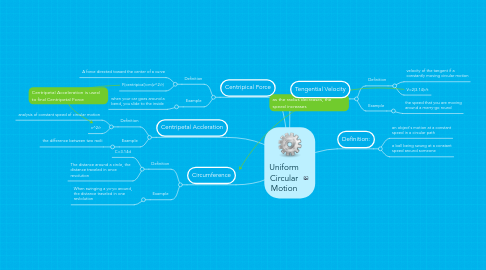

1. Centripical Force
1.1. Definition
1.1.1. A force directed toward the center of a curve
1.1.2. F(centripical)=m(v^2/r)
1.2. Example
1.2.1. when your car goes around a bend, you slide to the inside
2. Centripetal Accleration
2.1. Definition
2.1.1. analysis of constant speed of circular motion
2.1.2. v^2/r
2.2. Example
2.2.1. the difference between two radii
3. Circumference
3.1. Definition
3.1.1. C=3.14d
3.1.2. The distance around a circle, the distance traveled in once revolution
3.2. Example
3.2.1. When swinging a yo-yo around, the distance traveled in one revlolution
4. Tengential Velocity
4.1. Definition
4.1.1. velocity of the tangent if a constantly moving circular motion
4.1.2. V=2(3.14)r/t
4.2. Example
4.2.1. the speed that you are moving around a merry-go round

