Unit 3
by Osvaldo Perez
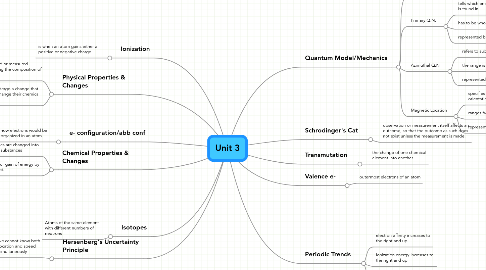

1. Ionization
1.1. is when an atom gains either a positive or negative charge
2. Hersenberg's Uncertainty Principle
2.1. we cannot know both location and speed simultaneously
3. Physical Properties & Changes
3.1. can be observed or measured without changing the composition of matter.
3.2. objects undergo a change that does not change their chemical nature
4. Isotopes
4.1. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
5. e- configuration/abb conf
5.1. how electrons would be organized in an atom
6. Chemical Properties & Changes
6.1. substances are changed into different substances
6.2. release or gain of energy by an object.
7. Quantum Model/Mechanics
7.1. Quanta:
7.1.1. Smallest measureable unit
7.2. Primary Q.N.
7.2.1. tells which energy level an e- is found in
7.2.2. has to be whole numbers
7.2.3. represented by n
7.3. Azimuthal Q.N.
7.3.1. refers to subshell"shape-type"
7.3.2. the range is from 0-n
7.3.3. represented by l
7.4. Magnetic Location
7.4.1. specifies the exact orbital by orientation if the subshell
7.4.2. ranges from -l to l
7.4.3. represented by m sub l
