1. Network Technologies
1.1. Hardware
1.1.1. Routers
1.1.2. Hubs
1.1.3. Switches
1.1.4. Gateways
1.1.5. Accesspoints
1.1.6. Modems
1.1.6.1. Plain old telephone service
1.1.6.2. Cable
1.1.6.3. DSL
1.2. Protocols
1.2.1. Internet
1.2.1.1. TCP
1.2.1.2. IP
1.2.1.2.1. 127.0.0.1
1.2.1.2.2. 192.168.1.x
1.2.1.2.3. Port 80
1.2.1.3. TelNet
1.2.1.4. VOIP
1.2.2. Mail
1.2.2.1. SMTP
1.2.2.2. POP3
1.2.2.3. IMAP
1.2.2.4. Webmail
1.2.3. Newsgroup
1.2.3.1. NNTP
1.2.4. Files
1.2.4.1. FTP
1.2.4.2. SFTP
1.2.5. Web
1.2.5.1. HTTP
1.2.5.2. HTTPS
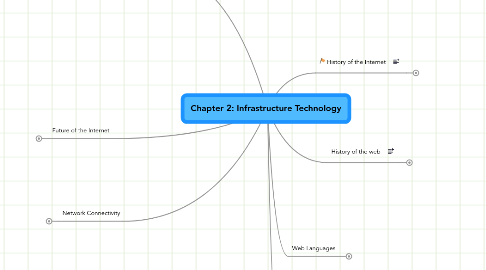
2. Future of the Internet
2.1. Internet2
2.2. Semantic Web
3. Network Connectivity
3.1. Public
3.2. Private
3.3. Bandwitdth
3.3.1. Telephone
3.3.1.1. POTS
3.3.1.2. ISDN
3.3.2. Broadband
3.3.2.1. Cable
3.3.2.2. DSL
3.3.3. Leased-line
3.3.3.1. T1/T3
3.3.3.2. ATM/OC3
3.3.4. Wireless
4. History of the web
4.1. 1945: Vannevar Bush- Memex
4.2. 1960's: Ted Nelson - Hypertex
4.3. 1987: Ted Nelson- Xanadu
4.4. 1989: Tim Berners Lee: WWW
4.5. 1993: Marc Andreesen- Mosaic
4.6. 1994: Andreesen & Clark: Netscape
4.7. 2004: Web 2.0
5. History of the Internet
5.1. 1960's: Dept of Defense
5.2. 1969: ARPANet
5.3. 1972: Email
5.4. 1979: Usenet
5.5. 1980s: NSF
5.6. 1993L CBC Peter Mansbridge
5.7. 1995: Privatized
5.8. 1974: TCP/IP
5.8.1. Vintin Cerf (Grandfather of internet)
6. Web Languages
6.1. SGML
6.1.1. HTML
6.1.2. DHTML
6.1.3. XML
6.1.4. XHMTL
6.2. CSS
6.3. Scripting and programming
6.3.1. Java
6.3.2. PEd
6.3.3. PHP
6.3.4. Python
6.3.5. Javscript
6.3.5.1. AJAX
6.3.5.2. Clinet-side
6.3.5.3. Server-Side
6.3.6. VBScript
7. Web Software
7.1. Web Servers
7.1.1. Apache
7.1.2. ISS
7.1.3. HFS
7.1.4. Server2Go
7.1.5. EasyPHP
7.1.6. XAMPP
7.2. Web Clients
7.2.1. Internet Explorer
7.2.2. Mozilla Firefox
7.2.3. Opera
7.2.4. Flock
