1. Natural and Man-Made Debris
1.1. Physical Damage to Spacecraft
2. Energetic Solar Flare Event
2.1. X-Ray Event
2.1.1. Spacecraft Charging and Discharge
2.1.2. Heating and Expansion of Upper Atmosphere
2.1.2.1. Increased N. Density and Drag (LEO sats)
2.1.3. Sudden Ionospheric Disturbance
2.1.3.1. Spacecraft Commanding Problems
2.1.3.2. Range Errors on LF and VLF Nav Systems
2.1.3.3. Short Wave Fadeout
2.1.3.4. Fluctuating Total Electron Current (TEC)
2.1.3.4.1. Location Errors on Navstar GPS
2.1.3.4.2. Radar Range, Rate, and Direction Error
2.1.3.4.3. Scintillation on Transionospheric Paths
2.2. High Energy Solar Particles (CME)
2.2.1. Radio Burst
2.2.1.1. Radio Frequency Interference
2.2.2. X-Ray Event/Radio Burst/Optical Flare
2.2.2.1. Hazard to Exposed Humans in Space
2.2.2.2. Single Event Upset (SEU), Sat Disorientation
2.2.2.3. False Star Sensor Data, Control Problems
2.2.2.4. Internal Sat Charging/Damage to Electronics
2.2.2.5. Deterioration of Spacecraft Surface
2.2.2.6. Medium Energy Particles
2.2.2.6.1. Deterioration of Spacecraft Surface
2.2.2.6.2. Spacecraft Charging/Discharge
2.2.2.6.3. Internal Sat. Charging/Damageof Electronics
2.2.2.6.4. Geostationary Magnetopause Crossing (GMC)
2.2.2.6.5. Direct Thermal Input to Low Temp. Systems
2.2.2.7. Polar Cap Absorption Event
2.2.2.7.1. Sever Degraded HF Propagation at High Lat
2.2.2.7.2. Range Errors on LF and VLF Nav Sys
3. Auroral Zone
3.1. Radar Auroral Clutter, Noise, Interference
3.2. Non-Great Circle HF Propogation
3.3. Fluctuating Total Electron Current (TEC)
3.3.1. Radar Range, Rate, and Direction Error
3.3.2. Location Errors on Navstar GPS
3.3.3. Scintillation on Transionospheric Paths
3.3.3.1. Signal Fade, Polarization, and Change in Phase
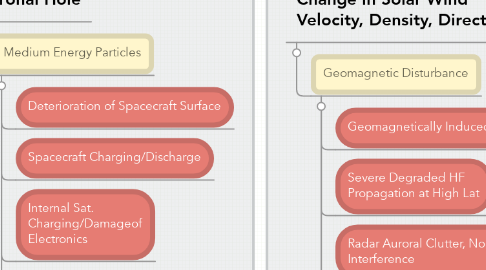
4. Coronal Hole
4.1. Medium Energy Particles
4.1.1. Deterioration of Spacecraft Surface
4.1.2. Spacecraft Charging/Discharge
4.1.3. Internal Sat. Charging/Damageof Electronics
4.1.4. Geostationary Magnetopause Crossing (GMC)
4.1.5. Direct Thermal Input to Low Temp. Systems
5. Change in Solar Wind Velocity, Density, Direction
5.1. Geomagnetic Disturbance
5.1.1. Geomagnetically Induced Currents
5.1.2. Severe Degraded HF Propagation at High Lat
5.1.3. Radar Auroral Clutter, Noise, Interference
5.1.4. Heating and Expansion of Upper Atmosphere
5.1.4.1. Increased N. Density and Drag (Leo Stats)
5.1.5. Fluctuating of Total Electron Current (TEC)
5.1.5.1. Location Errors on Navstar GPS
5.1.5.2. Radar Range, Rate, and Direction Error
5.1.5.3. Scintillation of Transionospheric Paths
5.1.5.3.1. Signal Fade, Polarization, and Change in Phase
6. Rayleigh-Taylor Instability
6.1. Equatorial Plasma Bubbles
6.1.1. Scintillation of Communication Signals
