E10: Smog
da Katie Leven
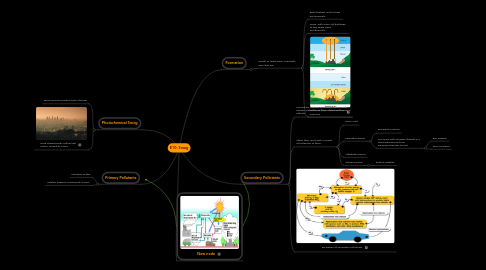

1. Photochemical Smog
1.1. Most common modern type of smog
1.2. Note characteristic yellow/red colour, caused by VOCs
2. Primary Pollutants
2.1. Nitrogen oxides
2.2. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
3. New node
4. Formation
4.1. Usually in large cities, especially ones that are:
4.1.1. Bowl-shaped, as this traps air/chemicals,
4.1.2. Large, with many tall buildings, as this again traps air/chemicals,
4.1.3. Suffering from a temperature inversion.
5. Secondary Pollutants
5.1. Formed by reaction of oxygen radicals with oxygen and water to form ozone and hydroxyl radicals.
5.2. These then react with a variety of molecules to form...
5.2.1. Nitric Acid
5.2.2. Peroxides ROOR
5.2.2.1. Extremely reactive
5.2.2.2. Can react with nitrogen dioxide in a Chain Reaction to form peroxyacylnitrates (PANs)
5.2.2.2.1. Eye irritants
5.2.2.2.2. Toxic to plants
5.2.3. Aldehydes RCHO
5.2.4. Ketones RCOR
5.2.4.1. Reduce visibility
