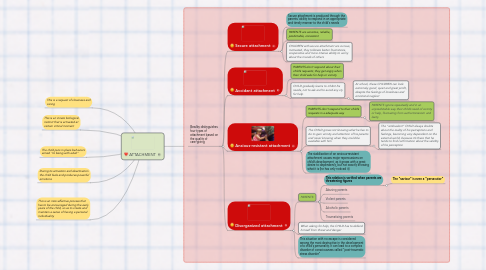
1. This is an inter-affective process that has to be encouraged during the early years of the child, so as to create and maintain a sense of having a personal individuality
2. This is an innate biological instinct that is activated at certain critical moment
3. During its activation and deactivation the child feels and produces powerful emotions
4. The child puts in place behaviors aimed "to being with adult"
5. This is a request of closeness and caring
6. Bowlby distinguishes four types of attachment based on the quality of care-giving
6.1. Secure attachment
6.1.1. Secure attachment is produced through the parents' ability to respond in an appropriate and timely manner to the child's needs
6.1.2. PARENTS are sensitive, reliable, predictable, consistent
6.1.3. CHILDREN with secure attachment are curious, motivated, they tollerate better frustrations, cooperative and more intense ability to worry about the moods of others
6.2. Avoidant attachment
6.2.1. PARENTS don’t respond about their child’s requests; they get angry when their child asks for help or vicinity
6.2.2. CHILD gradually learns to inhibit his needs, not to ask and to avoid any cry for help
6.2.2.1. At school, these CHILDREN can look extremely good, quiet and great profit, despite the feelings of loneliness and emotional neglect
6.3. Anxious-resistant attachment
6.3.1. PARENTS don’t respond to their child’s requests in a adequate way
6.3.1.1. PARENTS ignore repeatedly and in an unpredictable way their child’s need of vicinity or help, fluctuating from authoritarianism and laxity
6.3.2. The CHILD grows not knowing what he has to do to gain vicinity and attention of his parents and never knowing when they could be available with him
6.3.2.1. The “ambivalent” CHILD always doubts about the reality of his perceptions and feelings, becoming very dependent on the external world, because it’s there that he tends to find confirmation about the validity of his perception
6.3.3. The stabilization of an anxious-resistant attachment causes major repercussions on child’s development, as it grows with a great desire to dependency, but not exactly knowing what it is (he has only noticed it)
6.4. Disorganized attachment
6.4.1. PARENTS:
6.4.1.1. This relation is verified when parents are threatening figures
6.4.1.1.1. The “saviour” is even a “persecutor”
6.4.1.2. Abusing parents
6.4.1.3. Violent parents
6.4.1.4. Alcoholic parents
6.4.1.5. Traumatizing parents
6.4.2. When asking for help, the CHILD has to defend himself from threat and danger
6.4.3. This situation with no escape is considered among the most destructive in the development of a child's personality. It can lead to a complex disorder of consciousness called "post-traumatic stress disorder"

